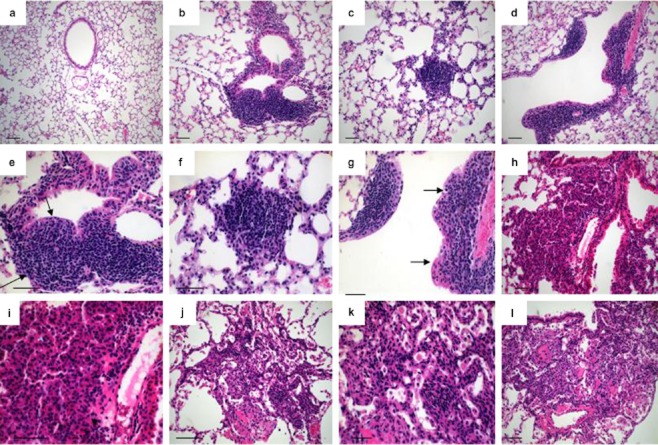
Figure 4.
Histological analysis of distinct types of lesions and stages of tumor progression in Lox-Cul4A mice. (a) Eight weeks post-infection with Ade-green fluorescent protein (GFP. (b) Slightly atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of terminal (bottom) and epithelial hyperplasia (EH) of a respiratory (top) bronchiole in Lox-Cul4A lungs eight weeks post-infection; (c) Small papillary adenoma in Lox-Cul4A lungs 12 weeks post-infection. (d) Moderate EH of a terminal bronchiole 16 weeks post-infection; arrow indicates the destroyed basal membrane. (e) Higher magnification of the lesion in B; arrows indicate the lesions. (f) Higher magnification of the lesion in (c). (g) Higher magnification of the lesion in (d). (h) Nonmucinous minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA). This subpleural adenocarcinoma tumor consists primarily of lepidic growth area of invasion 20 weeks post-infection. (i) Higher magnification of the lesion in (h). (j) Mucinous MIA 24 weeks post-infection. This consists of a tumor showing lepidic growth. (k) Higher magnification of the lesion in (j). The tumor cells grow mostly in a lepidic pattern along the surface of alveolar walls. (l) The tumor invades the areas of stromal fibrosis in an acinar pattern. Scale bar indicates 100 μm.