Figure 4.
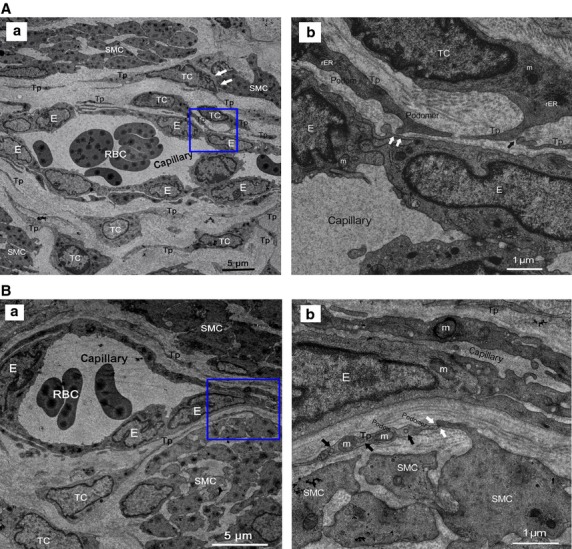
Normal TCs and Tps distributed in perivascular space or SMCs bundles. RBC: red blood cells; E: vascular endothelial cells. (A) Perivascular TCs. (a) A number of TCs, by their extremely long/thin Tps, surrounded and formed an almost complete circle around capillaries. Tps was composed of podoms and podomers. TCs established heterocellular contact with SMCs (white arrows). Mitochondria (m), rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) and secretory granules can be observed. (b) Higher magnification of the boxed area; TCs frequency formed homocellular junctions (black arrow) and heterocellular junctions (white arrows) with E. (B) Perivascular TCs. (a) TCs surrounded capillaries and scattered among SMCs. b higher magnification of the boxed area. (b) Abundant mitochondria (m) and microvesicles (black arrows) contained in podom. Tps established heterocellular contacts with SMCs (white arrows).
