Fig. 5.
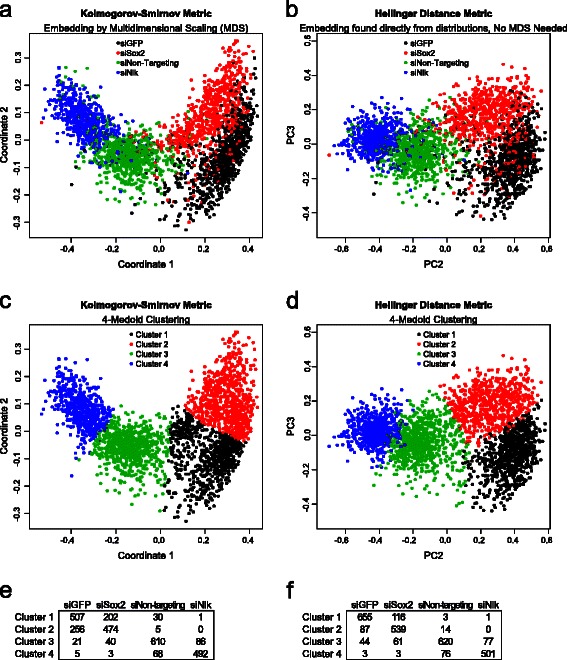
Comparison of Euclidean embedding constructed from either Kolmogorov-Smirnov distances or Hellinger distances. a For a subset of 2800 control wells, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov distance was computed for all pairs of distributions and multidimensional scaling (MDS) applied to compute a Euclidean embedding. The first two dimensions of the embedding were plotted for the given controls. b For the same controls, the Hellinger distances were used to directly generate a Euclidean embedding and the second and third PCs plotted (the first PC represents overlap with the null effect). The first 4 dimensions of the (c) Kolmogorov-Smirnov distance embedding and (d) the Hellinger distance embedding into 4 medoids were clustered and plotted as in panels a and b. Table of overlap between clustering and true identities of controls when using (e) Kolmogorov-Smirnov embedding or (f) Hellinger distance embedding
