Figure 5. Ion-induced conformational change in substrate binding site of GltPh.
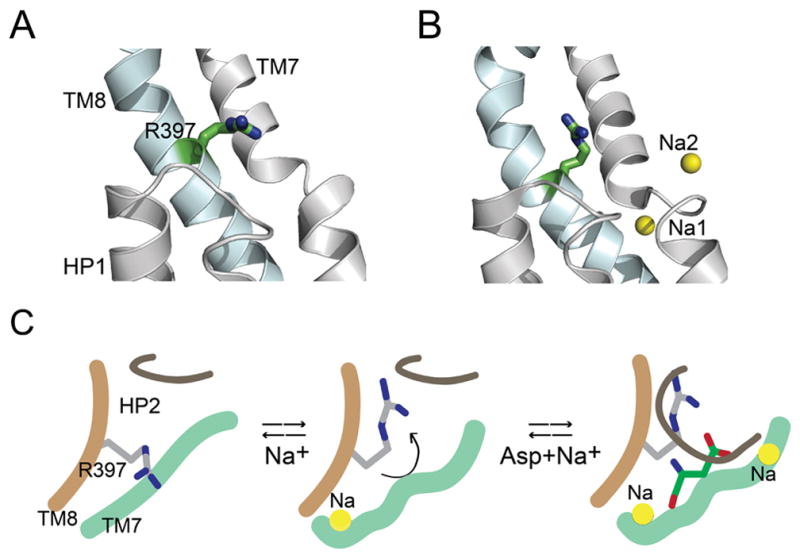
A and B) Crystal structures of the inward-facing conformation of GltPh in the apo-state (A, pdb: 4p19) and in the presence of Tl+ (B, pdb: 4p6h). Close-up view of the substrate binding site showing HP1 and TM7 (colored grey) and TM8 (blue). Arg397 is shown in stick representation. The cation-binding sites, Na1 and Na2 are represented as yellow spheres. C) Model depicting a proposed role for Arg397. Binding of a Na+ ion causes a conformational change in the substrate binding site that reorients Arg397 to create a high affinity Asp binding site. Binding of Asp is followed by the binding of another Na+ ion that is concomitant with the closure of HP2 leading to transport. Only the sodium sites visualized in the GltPh crystal structures 9 are shown in the model.
