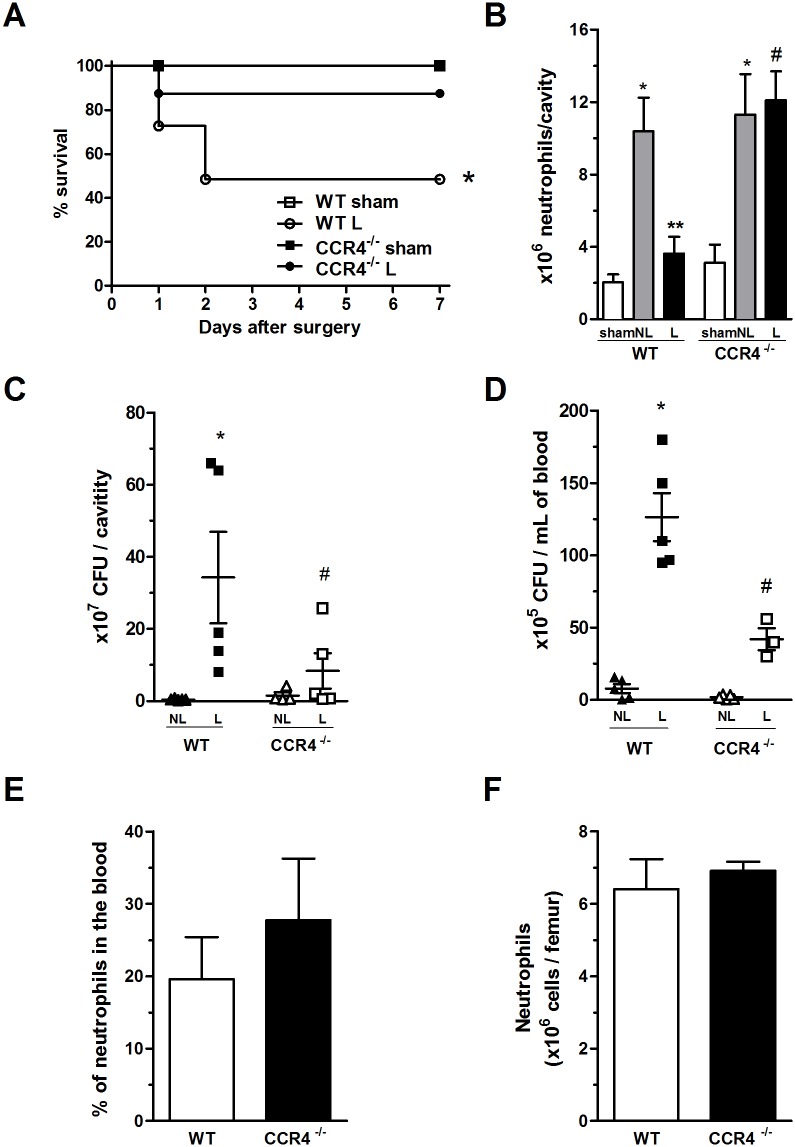
Fig 1. CCR4-/- mice show increased resistance to severe sepsis.
(A) WT (open symbols) and CCR4-/- (filled symbols) mice underwent sham (square) or L-CLP (circle) surgery. All groups received antibiotic therapy of ertapenem (75 mg/kg) at 6, 24 and 48 h after surgery. The survival of these mice was followed until day 7. The data are representative of four experiments (n = 7–11 mice per group). *P<0.05 between the CLP CCR4-/- and CLP WT groups. (B) Neutrophil migration to the peritoneal cavity in the sham, Non-Lethal CLP (NL) and Lethal-CLP (L) groups evaluated at 6 h after surgery. *P<0.05 between the NL-CLP and sham groups of both strains (WT and CCR4-/-); **P<0.05 between L-CLP and NL-CLP groups of WT mice; and #P<0.05 between the L-CLP WT and L-CLP CCR4-/- mice. (C) Bacterial counts in peritoneal exudate and (D) blood at 6 h after NL- or L-CLP surgery of the WT and CCR4-/- mice. *P<0.05 between the L-CLP WT and NL-CLP WT groups; and #P<0.05 between the L-CLP CCR4-/- and L-CLP WT groups. (E) Percentages of neutrophils in the blood of naïve WT and CCR4-/- mice. (F) Absolute numbers of neutrophils in the bone marrow of naïve WT and CCR4-/- mice.