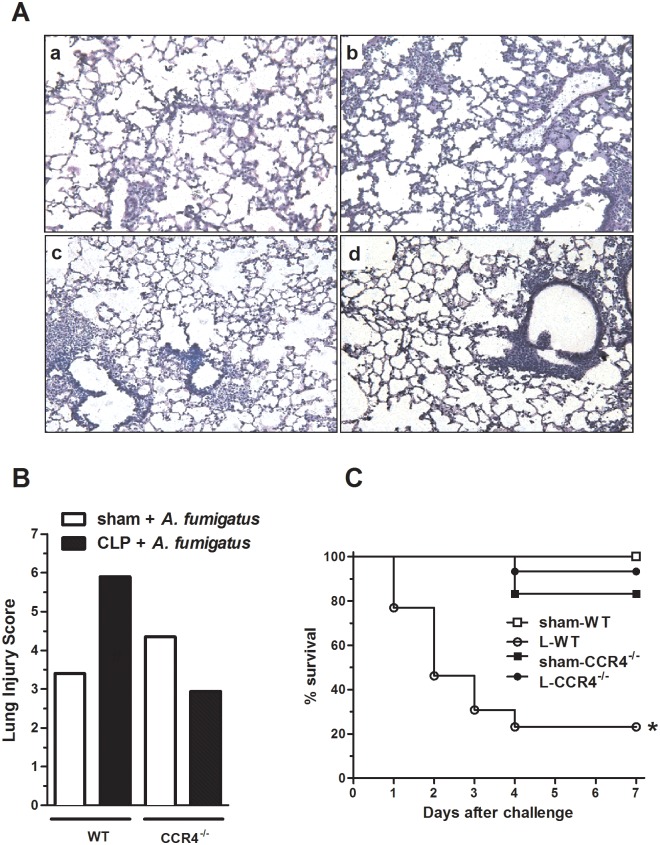
Fig 5. CCR4-/- post-septic mice present a better survival rate and reduced lung damage after A. fumigatus challenge.
The WT and CCR4-/- mice were subjected to sham or CLP surgery and received antibiotic treatment with ertapenem (75 mg/kg) at 6, 24 and 48 h after surgery. On day 4 after surgery, the surviving CLP and sham mice were challenged with 7.5 x 107 of A. fumigatus conidia i.t. (60–70% of the survivors after CLP surgery represented 100% of the mice at time 0). (A) On day 4 after surgery, the sham-WT, L-WT, sham-CCR4-/-, and L-CCR4-/- mice were challenged with A. fumigatus, and after 48 h, all mice were euthanized, and their lungs were collected for histology. The lungs were fixed, and 5-μm sections were stained with H&E. (B) Histological appearances were scored for perivascular, peribronchial, septal, and alveolar edema and for perivascular, interstitial, and alveolar cell infiltration. The pathological changes differed significantly between the L-WT and L-CCR4-/- groups. (C) Survival was followed until 7 days after fungal challenge. The data are representative of two experiments; n = 9–15 mice per group. *P<0.0001 compared with the L-WT group.