Fig. 4.
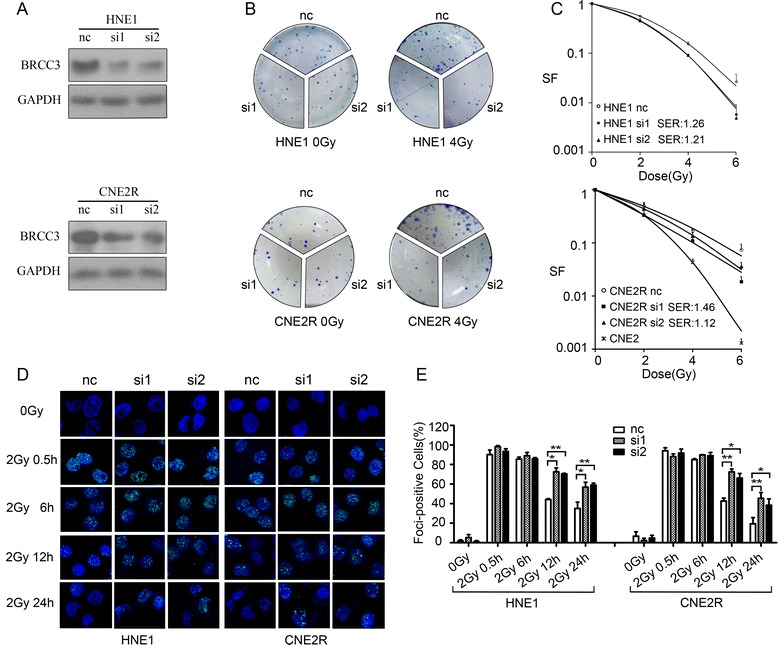
Depletion of BRCC3 results in increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation. a Knockdown of BRCC3 was assessed by western-blotting (nc: negative control siRNA; si1: siRNA1 target BRCC3; si2: siRNA2 target BRCC3). b HNE1 and CNE2R cells were transfected with siRNAs, 24 h later they were seeded to 6-well plates and irradiated with different doses. Clones were stained and counted after 7-14 days. c Dose-survival curves of irradiated HNE1 and CNE2R cells (range, 0-6Gy, SF: survival fractions, SER: radiation sensitization enhancement ratio). In HNE1 cells SER of si1 and si2 was 1.26 (p < 0.05) and 1.21 (p < 0.05) separately; In CNE2R cells SER of si1 and si2 was 1.46 (p < 0.01) and 1.12 (p < 0.05) separately. d Immunofluorescent staining of γH2AX. HNE1 and CNE2R cells transfected with BRCC3 or control siRNA was exposed to 2Gy irradiation, and immunofluorescent staining of γH2AX foci was conducted before and 0.5 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h after irradiation (e) Quantification of γH2AX foci formation. A positive cell was determined by the presence of >10 foci/cell. The percentage of positive cells was compared by t-test. The asterisks indicate a significant (*p < 0.05,**p < 0.01) difference
