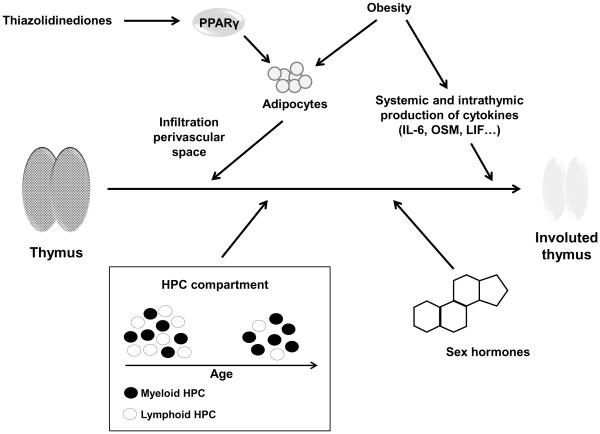
Figure 1. Mechanisms in thymic involution.
Traditionally, increased production of sex hormones, intrathymic production of inflammatory mediators and the age-dependent change in lineage commitment of hematopoietic stem cells have been associated with thymic involution. Recently identified accelerators of thymic involution are obesity and possibly PPARγ (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma) stimulators that are routinely used in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus and that support adipocyte differentiation and invasion into the perivascular space.