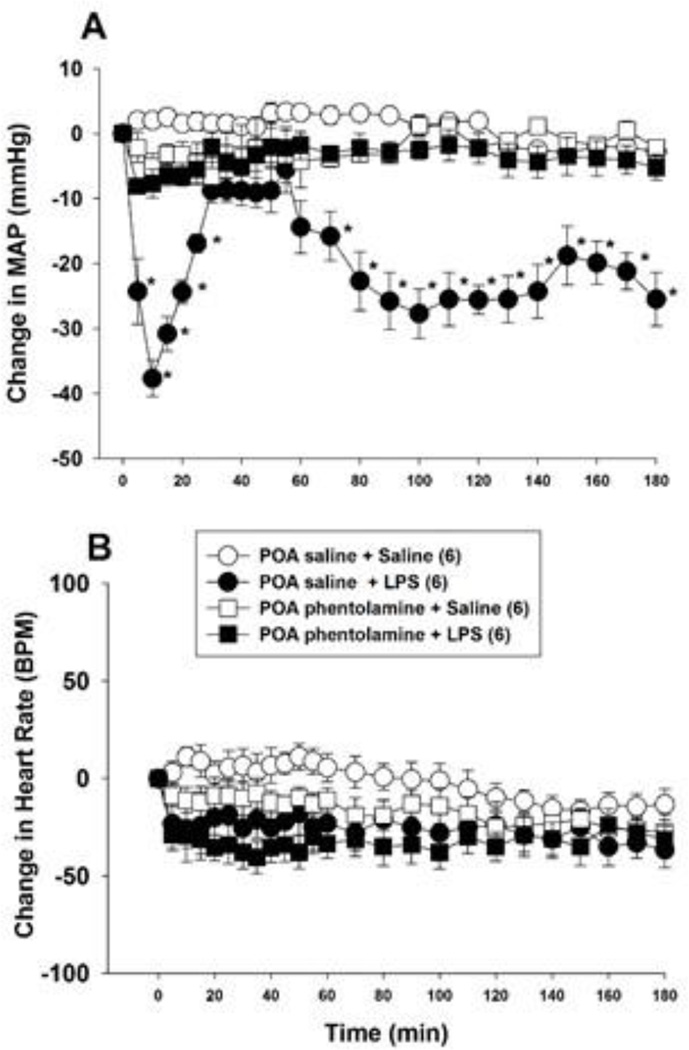
Figure 2.
Bilateral phentolamine injection into the POA inhibits the hypotension produced by i.v. LPS (15 mg/kg) injection. Phentolamine (5 µg/µl) or saline (1 µl) was injected into the POA of anesthetized rats bilaterally and, 2 min later, LPS or saline was administered i.v. Mean arterial pressure (MAP; panel A) and heart rate (panel B) were monitored for 180 min. The numbers in parentheses indicate the number of animals in each group. Baseline MAP and heart rate values were: POA saline + i.v. saline = 109.8 ± 4.2 mmHg and 361 ± 25 BPM; POA saline + i.v. LPS = 112.2 ± 3.7 mmHg and 371 ± 19 BPM; POA phentolamine + i.v. saline = 105.1 ± 2.9 mm Hg and 377 ± 31 BPM; POA phentolamine + i.v. LPS = 114.5 ± 4.1 mmHg and 325 ± 12 BPM. Data were analyzed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. *, P < 0.05, significantly different from the POA saline plus i.v. saline treated group. BPM = beats per minute.