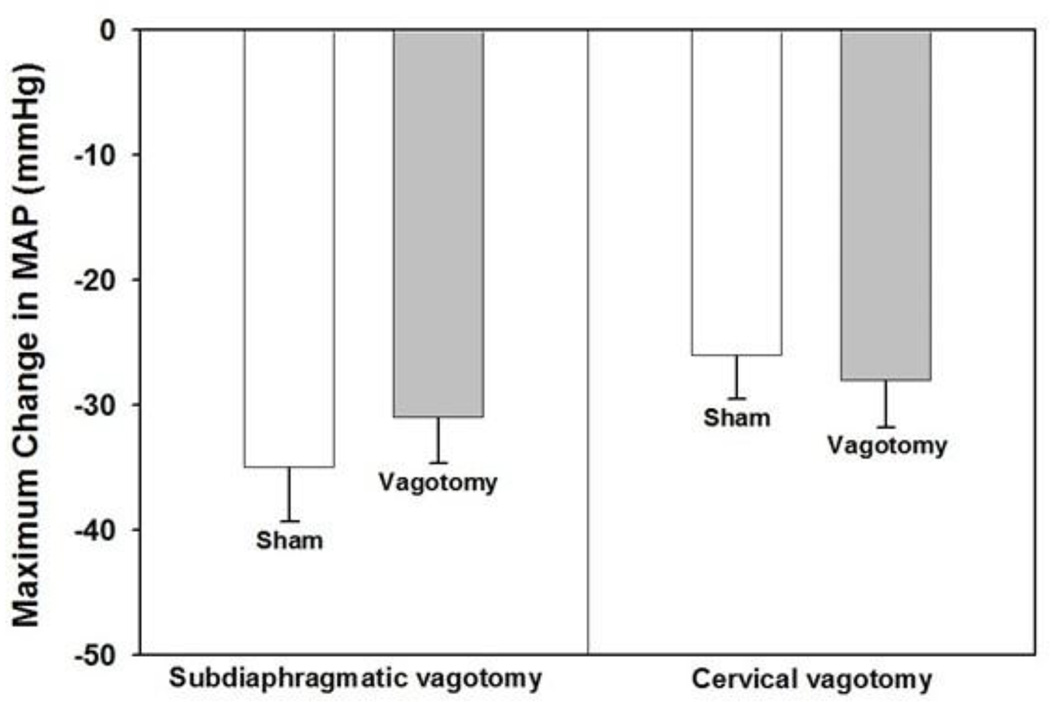
Figure 3.
Neither subdiaphragmatic nor cervical vagotomy inhibit the hypotension evoked by LPS. Subdiaphragmatic or cervical vagotomy was performed 15 min before rats were administered LPS (15 mg/kg) or saline i.v. and mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate were monitored for 60 min (n = animals in each group). Baseline MAP values for subdiaphragmatic vagotomy were: sham vagotomy + LPS = 110.5 ± 3.3 mmHg; vagotomy + LPS = 106.6 ± 3.2 mmHg. Baseline MAP for cervical vagotomy were: sham vagotomy + LPS = 121.5 ± 6.7 mmHg; vagotomy + LPS = 111.9 ± 5.8 mmHg. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM maximum change in MAP after LPS administration and were analyzed with two-way repeated measure ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.