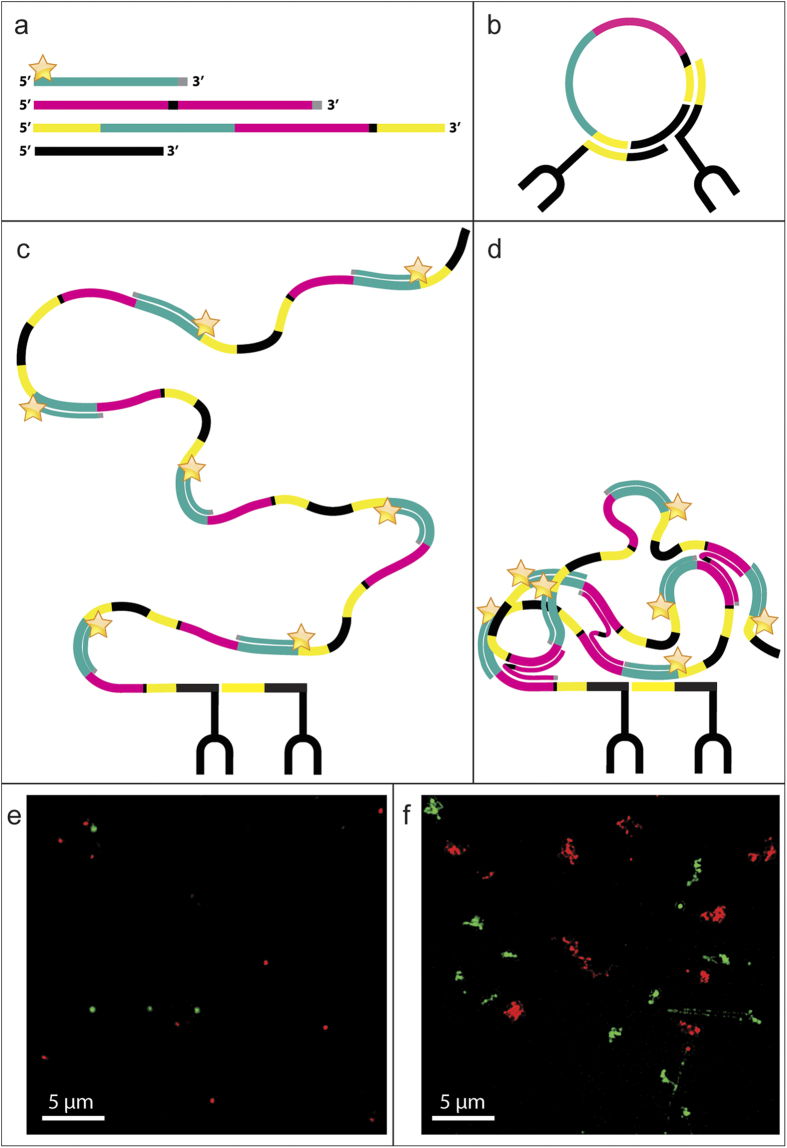
Figure 1.
Schematic cartoon and visualisation of regular vs. compacted RCPs. The oligonucleotides from top to bottom in (a) are the detection oligonucleotide, the compaction oligonucleotide, the long circularization oligonucleotide and the short circularization oligonucleotide. The detection oligonucleotide (Table 1, oligonucleotide A) has the same sequence as a part of the long circularization oligonucleotide (cyan), nucleotides preventing degradation and priming (grey) by the polymerase and a fluorophore (star). The compaction oligonucleotide (Table 1, oligonucleotide B) has two copies of the same sequence also found in the long circularization oligonucleotide (magenta), a spacer sequence (black) and nucleotides preventing degradation and priming (grey). Apart from the already mentioned sequences, the long circularization oligonucleotide (Table 1, oligonucleotide C) also has a spacer sequence (black) and parts hybridizing to the PLA probes (yellow). The short circularization oligonucleotide (oligonucleotide D in Table 1) has a sequence complementary to each PLA probe (not colored), spaced apart by a short sequence (not colored). The circularization oligonucleotides are ligated together in a separate step preceding the RCA reaction, resulting in (b). In regular RCA, the fluorophore labelled detection oligonucleotide is the only added oligonucleotide and the resulting RCP is depicted in (c). Adding also the compaction oligonucleotide to the RCA reaction results in a less dispersed RCA product (d). The bottom images were acquired with a 3D Structured Illumination Microscope and depict RCPs generated from two different circular templates with the dissimilarity of two different sequences for detection oligonucleotide hybridization. One of the detection oligonucleotides labelled with Alexa488 (green) and the other with Alexa642 (red). The images show RCPs with (e) and without (f) compaction oligonucleotide.