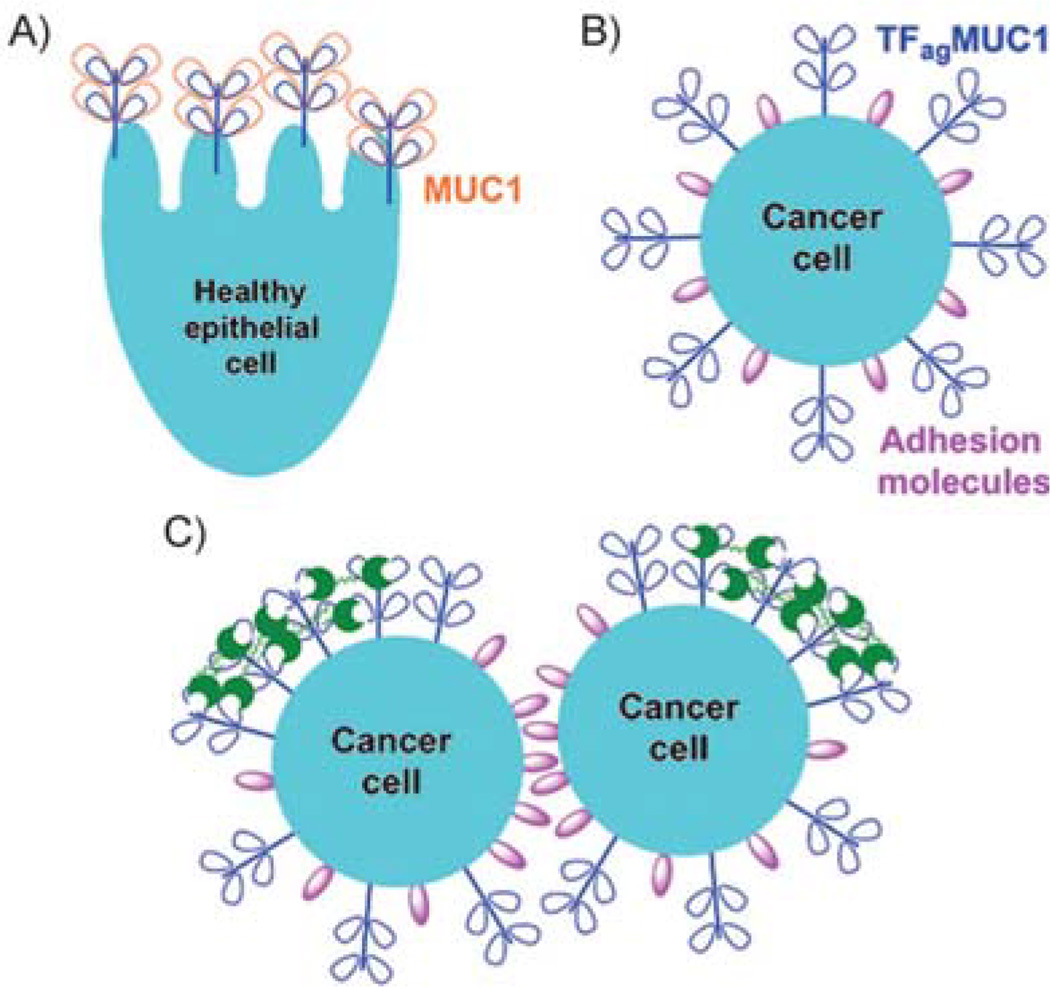
Figure 1.
Interaction of galectin-3 with MUC1 at the cell surface. A) A healthy epithelial cell with a normal distribution of MUC1. B) The surface of a cancer cell with over-expressed and aberrantly glycosylated MUC1. C) When circulating galectin-3 (green) is introduced to the cancer cell surface, its interaction with cancer-associated MUC1 causes adhesion molecules to be exposed, thus inducing aggregation (adapted from Yu et al.[17]).