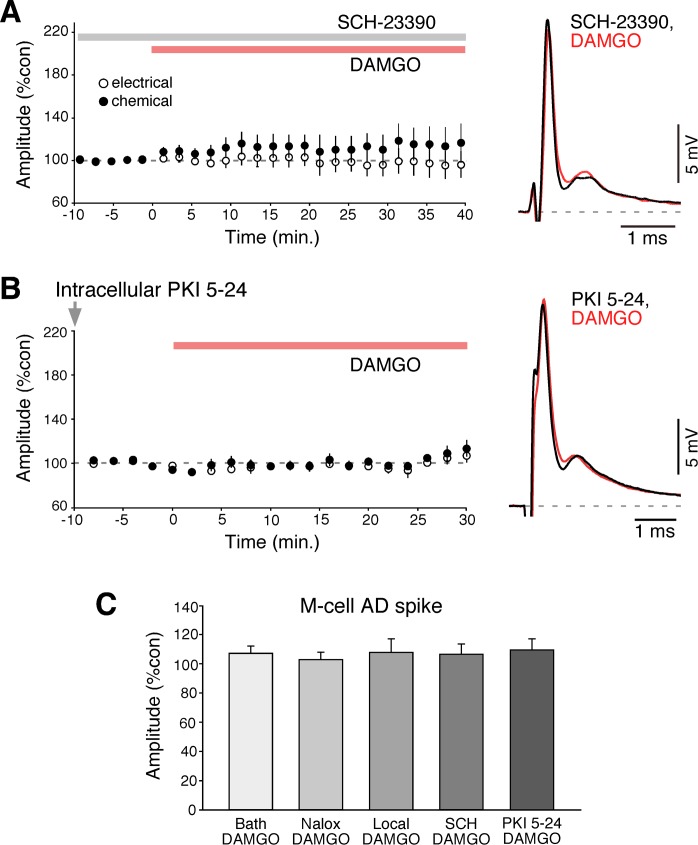
Fig. 3.
DAMGO-evoked potentiation requires activation of dopamine D1/5Rs. A: time course of both components of the mixed synaptic response for experiments in which bath application of DAMGO (red bar) followed pretreatment with the D1/5R antagonist SCH-23390 (gray bar, n = 5). B: time course for experiments in which the PKA inhibitor PKI 5-24 was applied intradendritically (gray arrow, 500 μM) prior to bath application of DAMGO (n = 5). C: neither bath or local application of drugs led to changes in the amplitude of the AD spike of the M-cell (an indicator of the M-cell input resistance), indicating that changes, when observed, were ascribable to modifications in the strength of electrical and chemical synapses. The M-cell AD spike averaged 107.4% after DAMGO application, 103.1% after Naloxone and DAMGO application, 111.2% after local DAMGO, 106.7% after SCH 23390 and DAMGO, and 109.9% after PKI 5-24 and DAMGO.