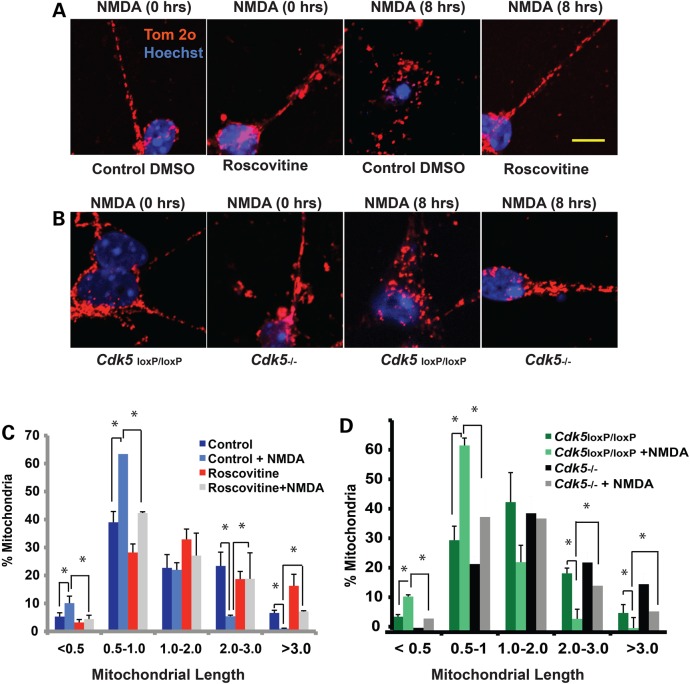
Figure 5.
Pharmacological inhibition of CDK5 or genetic deletion of CDK5 rescues mitochondrial fragmentation in NMDA-induced neuronal injury. (A) Cerebellar granule neurons were treated with 10 µm Roscovitine or DMSO control at 7 DIV for 3 h prior to exposure to NMDA (100 µm NMDA/10 µm Glycine). Following 8 h of treatment with NMDA, mitochondrial morphology was assessed using an antibody to Tom-20. Representative images of mitochondrial morphology under different treatment conditions are shown. (B). The cultured Cdk5−/− CGNs were obtained from Cdk5loxP/loxP cultures by addition of CRE adenoviruses at 5 DIV for 48 h. GFP adenoviruses were added to parallel cultures and used as control (referred to as Cdk5loxP/loxP). The neurons were treated with NMDA at 7 DIV as described in (A). Mitochondrial morphology was assessed using an antibody to Tom-20. Representative images of mitochondrial morphology under different treatment conditions are shown. (C and D) Mitochondrial length was measured and binned into different length categories and quantified as percentage. *P < 0.05; Mag bar, 10 µm.