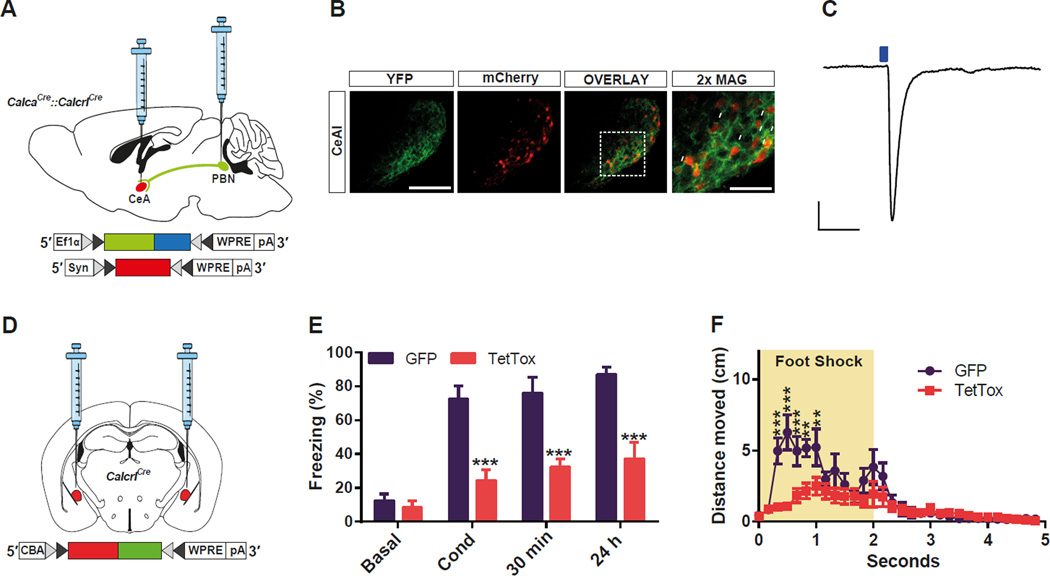
Figure 6. CGRPR Neurons in the CeAl Are Functionally and Anatomically Downstream of the PBel CGRP Neurons and Relay Teaching Signals during Threat Conditioning.
(A) Dual delivery of AAV carrying Cre-dependent ChR2 into the PBN of CalcaCre mice and AAV carrying Cre-dependent mCherry into the CeA in the CalcaCre::Calcrl Cre mouse.
(B) Representative histological images of the terminal projections of the PBN CGRP neurons to the CeAl, and their direct-recipient mCherry-labelled CGRPR neurons in the CeAl. White arrows indicate their characteristic perisomatic synapses in the CeAl.
(C) Example traces of photostimulation-evoked EPSCs in the mCherry-labelled CGRPR neurons in the CeAl. The average amplitude of the EPSC from 6 neurons (2 mice) was 51.6 pA ± 19.9. Scale bar: 25 pA, 25 ms.
(D) Bilateral delivery of AAV carrying Cre-dependent TetTox into the CeAl of CalcrlCre mice.
(E) Genetic silencing of CGRPR neurons in the CeAl by TetTox attenuated freezing responses immediately after conditioning (Cond) and 30 min or 24 h after contextual fear conditioning when compared with the GFP-expressing control mice.
(F) Immediate escape running response of the test mice to the foot shock was attenuated by functionally silencing the PBel CGRP neurons in the CalcaCre mice. All data shown are means ± s.e.m. from 7 mice per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.