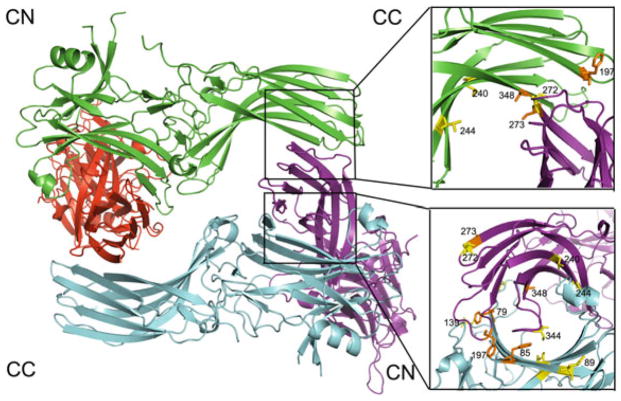
Fig. 1.
The crystallographic tetramer of arrestin-1. In the structure [PDB ID: 1CF1 (Hirsch et al. 1999)] each protomer is shown in a different color. The crystallographic tetramer is a dimer of dimers, where individual dimers are held together via C-to-N-domain interfaces (CN), and the two dimers form a tetramer via C-to-C-domain interfaces (CC). The interfaces are enlarged on the right, with residues in positions probed by site-directed spin labeling EPR (Hanson et al. 2007c, 2008a) shown as stick models. Color coding: the residues in positions where the behavior of the spin label was consistent with predictions based on the crystal structure are shown in orange; those in positions where the behavior of the spin label was inconsistent with crystal structure are shown in yellow. Note that at least half of the positions fall into the latter category