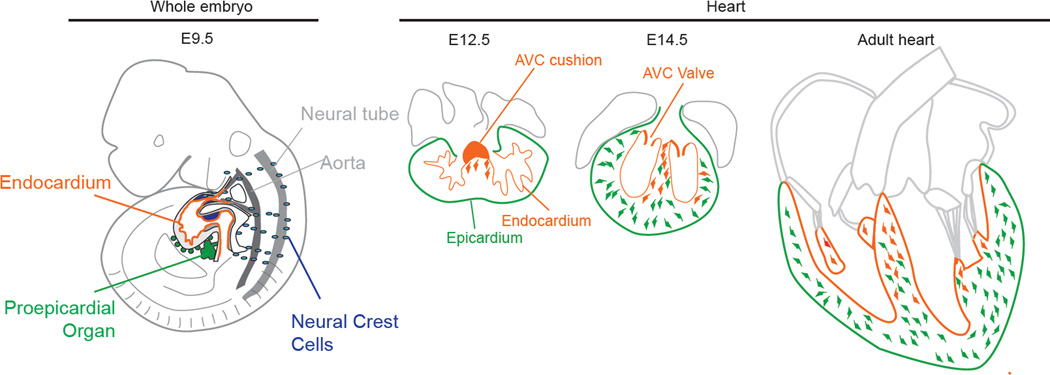
Figure 1.
Lineages giving rise to cardiac fibroblasts during embryonic development. Illustration of an E9.5 embryo showing the myocardium with its inner endocardium, the proepicardial organ and migrating neural crest cells. Fibroblasts derived from the AVC cushion (orange) first invade the septum at E12.5. Subsequently, epicardial EMT generates fibroblasts (green) that invade the free walls by E14.5. In adult heart, endothelially derived fibroblasts are found most abundantly in the septum, whereas epicardially derived fibroblasts populate the free walls.