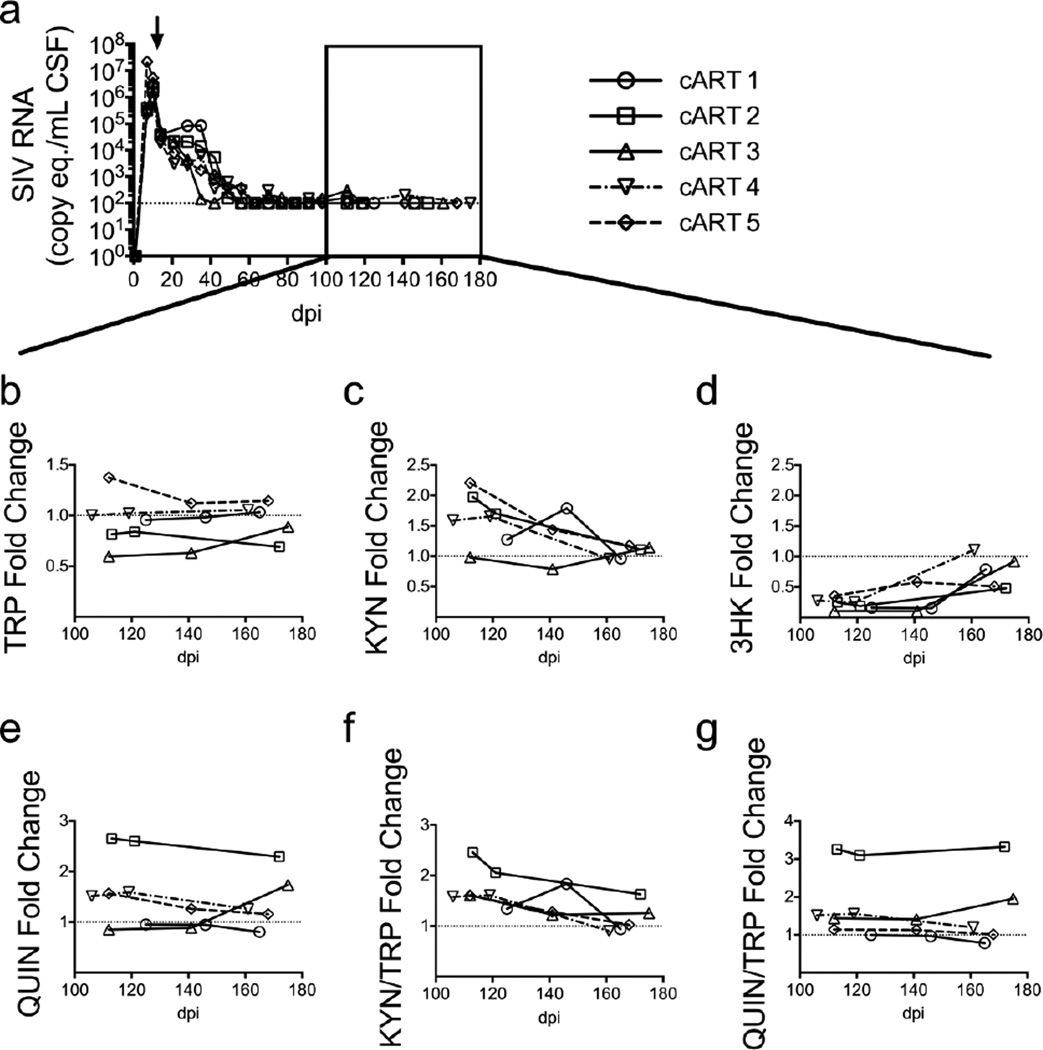
Fig. 6.
Low CSF QUIN/TRP ratios correspond with absence of neurological disease in well-suppressed, cART-treated animals. (a) Five SIV-infected macaques were treated with a 4-drug cART regimen beginning at day 12 p.i. (black arrow) that suppressed CSF viral loads to the limit of detection (100 copies/mL, represented by the dotted line) by 80 days p.i. The black box indicates time points during suppressive cART therapy at which metabolite levels were measured. (b – f) Three pre-infection CSF samples and three post-infection samples following suppression of CSF viremia to undetectable levels with cART were examined in each animal for levels of TRP (b), KYN (c), 3HK (d), and QUIN (e), and for KYN/TRP (f) and QUIN/TRP ratios (g). Data in graphs b through g are presented as fold change over the average of the pre-infection values for each macaque, designated by the dotted line. The viral load data displayed in (a) has been modified from a previously published version (Zink et al. 2010).