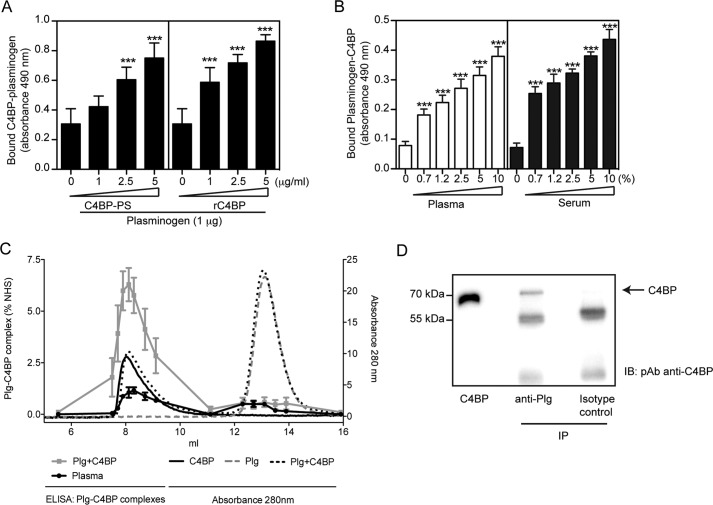
FIGURE 3.
C4BP forms complexes with plasminogen. A and B, interaction between C4BP and plasminogen. Polyclonal sheep anti-plasminogen (10 μg/ml, A) or polyclonal anti-C4BP Ab (10 μg/ml, B) were coated on 96-well microtiter plates. A mixture of plasminogen with plasma-purified C4BP-PS or rC4BP (A), or normal plasma or serum (B) were added. Bound C4BP-plasminogen complexes were detected with a polyclonal rabbit anti-C4BP Ab (A) and sheep anti-plasminogen Ab (B) and peroxidase-conjugated respective secondary Abs and substrate. A one-way analysis of variance test was used to calculate statistical significance. ns, not significant; ***, p < 0.001. C, rC4BP (0.2 mg/ml) and plasminogen (0.2 mg/ml) were incubated separately or together overnight at 37 °C and analyzed on a Superose 12 gel filtration column. The A280 nm for rC4BP (black solid line), plasminogen (gray dotted line), and rC4BP with plasminogen (black dotted line) are shown. Complexes of rC4BP and plasminogen were measured using a sandwich ELISA and plotted as percentage of complex present in normal human serum (gray squares). Furthermore, ELISA was used to detect C4BP-plasminogen complexes in pooled human plasma (black dots). ELISA data represent mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments performed in duplicates. D, protein G-coated-Sepharose beads where incubated with a monoclonal anti-plasminogen Ab, and then incubated with IgG-depleted normal serum. C4BP was detected by Western blotting under reduced conditions using a polyclonal anti-C4BP Ab. Isotype control Ab was used as negative control.