FIGURE 3.
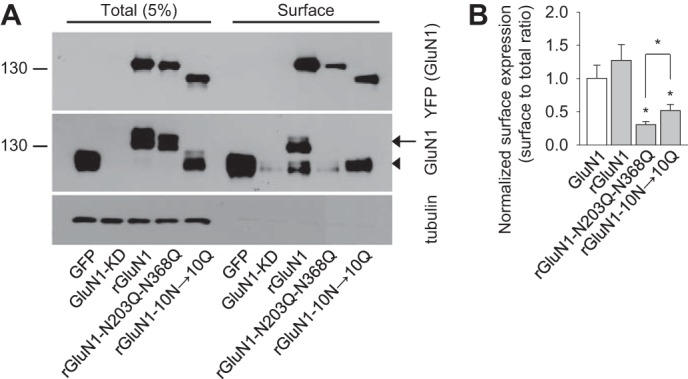
GluN1-N203Q-N368Q subunits have reduced surface expression in hippocampal neurons. A, example of a cell-surface biotinylation assay from dense cultures of hippocampal neurons infected with the following lentiviruses: control::GFP (GFP), GluN1-KD::GFP (GluN1-KD), GluN1-KD::YFP-rGluN1-1a (rGluN1), GluN1-KD::YFP-rGluN1-1a-N203Q-N368Q (rGluN1-N203Q-N368Q), or GluN1-KD::YFP-rGluN1-1a-10N→10Q (rGluN1-10N→10Q). The surface NMDARs were biotinylated and pulled down using streptavidin-agarose resin. Total input (5% of the lysate) and surface NMDARs were detected using anti-GluN1 and anti-GFP antibodies. Anti-tubulin antibody was used to confirm the integrity of the assay. In the GluN1 blot, the arrow indicates either rGluN1 or rGluN1-N203Q-N368Q. The arrowhead indicates either endogenous GluN1 or YFP-rGluN1-10N→10Q. B, summary of the band intensities of the surface and total NMDAR pools from the blots in A (n = 6). *, p < 0.05 versus wild-type rGluN1, analyzed by one-way ANOVA. The surface to total ratio of endogenous GluN1 level (GluN1), which was quantified from the anti-GluN1 blot, is included in the graph, together with the data obtained with the recombinant rGluN1 subunits (rGluN1, rGluN1-N203Q-N368Q, rGluN1-10N→10Q), quantified from the anti-YFP blot.
