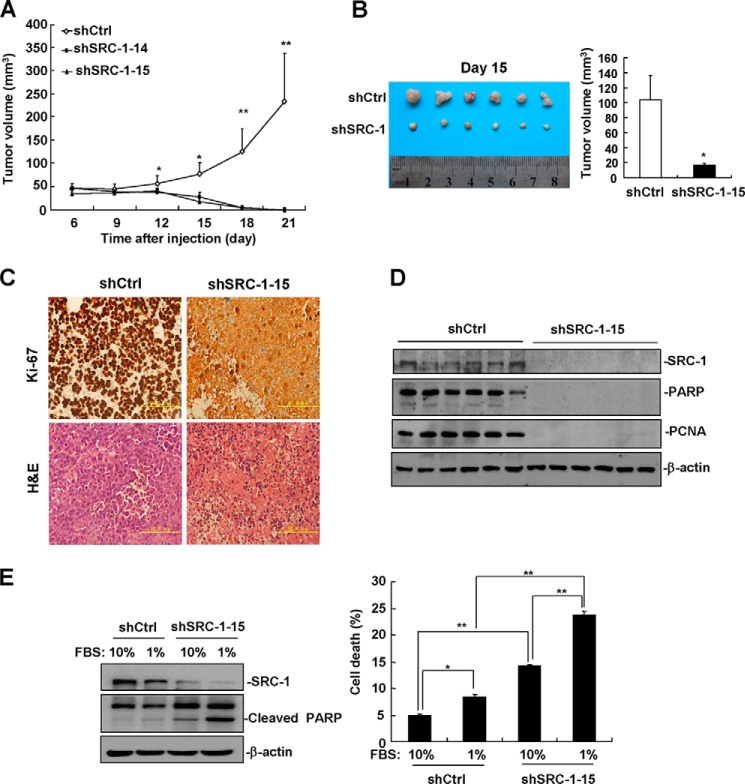
FIGURE 5.
Down-regulation of SRC-1 impairs xenograft tumor maintenance. A, knockdown of SRC-1 inhibited HCC cell tumorigenesis in vivo. Stable SRC-1-knockdown HepG2 cells and control cells were subcutaneously injected into the backs of nude mice. Beginning 6 days after cell injection, tumor volume was measured every 3 days. n = 5; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. This experiment was performed twice with similar results. B, on day 15 after injection, SRC-1-knockdown tumors showed a significant decrease in tumor volume compared with control tumors. An image of a tumor is shown. This experiment was performed twice with similar results. C, Ki-67 and H&E staining of tissue sections from SRC-1-knockdown and control tumors. A representative image is shown. D, the expression of the intranuclear proteins poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and PCNA is lost in SRC-1-knockdown tumors. This experiment was performed three times with similar results. E, down-regulation of SRC-1 significantly increased serum starvation-induced cell death. A total of 4 × 105 cells were seeded into 6-well plates and cultured with either 10% FBS or 1% FBS for 72 h. Both adherent and non-adherent cells were harvested for cell death detection. This experiment was performed three times with similar results. Error bars, S.E.