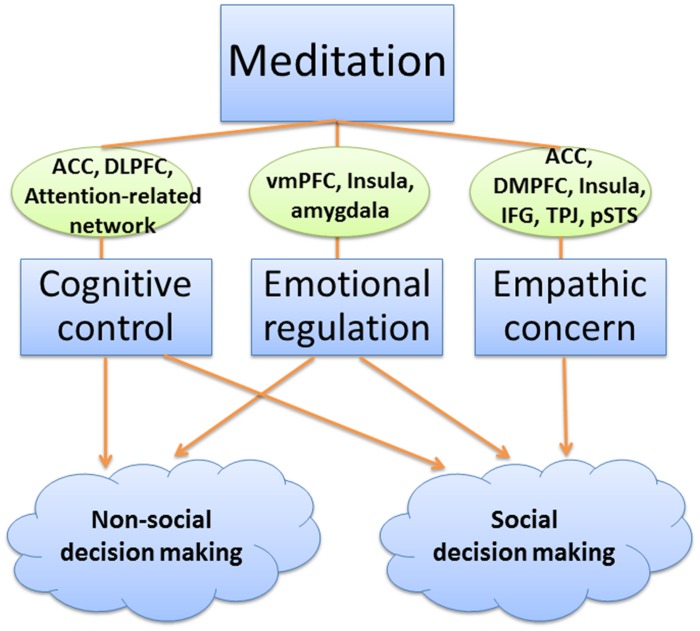
FIGURE 1.
A model for the effects of meditation on decision making. Meditation modulates brain activities associated with cognitive control, emotion regulation and empathy, and lead to improved non-social and social decision making. Our proposed model is a combination of existed behavioral and neuroimaging findings, theoretical guidance of dual-process theory, as well as proper speculations on the underlying mechanisms. Both the specific neural findings and the modulation effects of cognitive control, emotional regulation, and empathic concern between meditation and decision making are supported by extant research literature. However, more evidence is needed to explore the function of specific brain areas and their interaction effects on decision making during meditation training. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex; DLPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; dmPFC: dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; IFG: inferior frontal gyrus; pSTS: posterior superior temporal sulcus; TPJ: temporo-parietal junction; vmPFC: ventromedial prefrontal cortex.