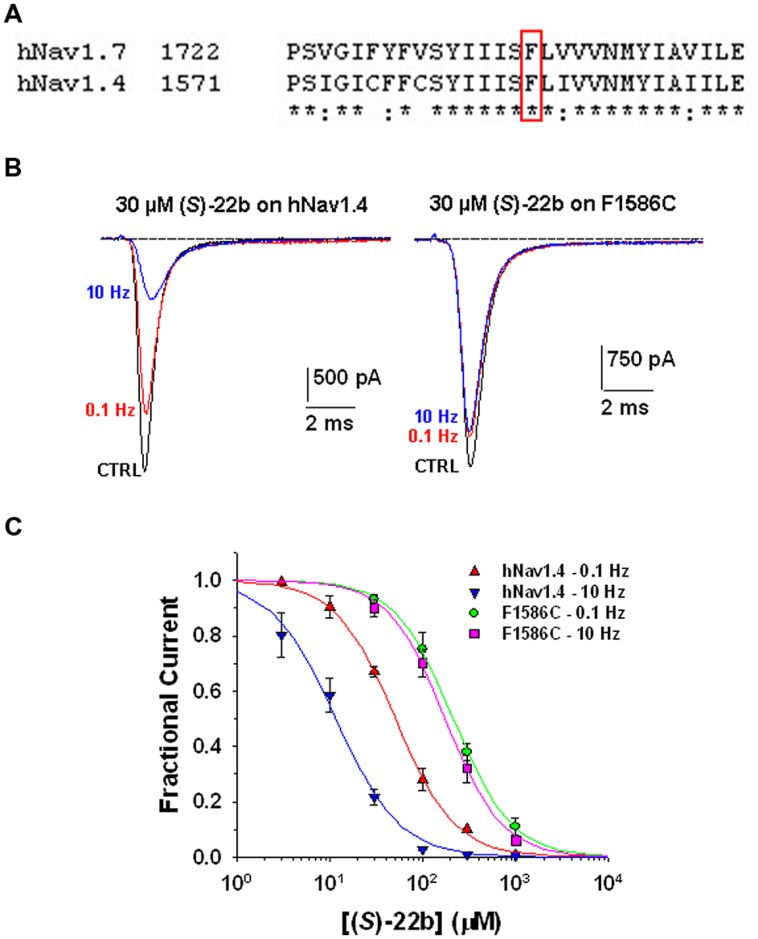
FIGURE 5.
Effects of (S)-22b on wild-type hNav1.4 channels and F1586C mutant. (A) Amino acid alignment of hNav1.7 and hNav1.4 using Clustal W 2.0 shows high conservation of the putative local anesthetic receptor located within the sixth segment of domain IV. The phenylalanine residue in red box (F1586 in hNav1.4 and F1737 in hnav1.7) is thought to be critical for the binding of local anesthetics to inactivated sodium channels. (B) Representative traces of sodium currents recorded as in Figure 2 in HEK29 cells permanently transfected with wild-type hNav1.4 or F1586C hNav1.4 mutant. The inhibitory effects of 30 μM (S)-22b were greatly reduced in the F1586C mutant. (C) Concentration–response relationships for (S)-22b at 0.1 and 10 Hz stimulation frequencies were obtained as in Figure 3, and fitted with Eq. 1. Each data point is the mean ± SEM of at least three cells. At both stimulation frequencies, the inhibition of F1586C channels by (S)-22b was significantly minor with respect to that of WT channels at 30, 100, 300, and 1000 μM (at least P < 0.05 with unpaired Student’s t-test). The fit parameters together with the SE of the regression are given in Table 1.