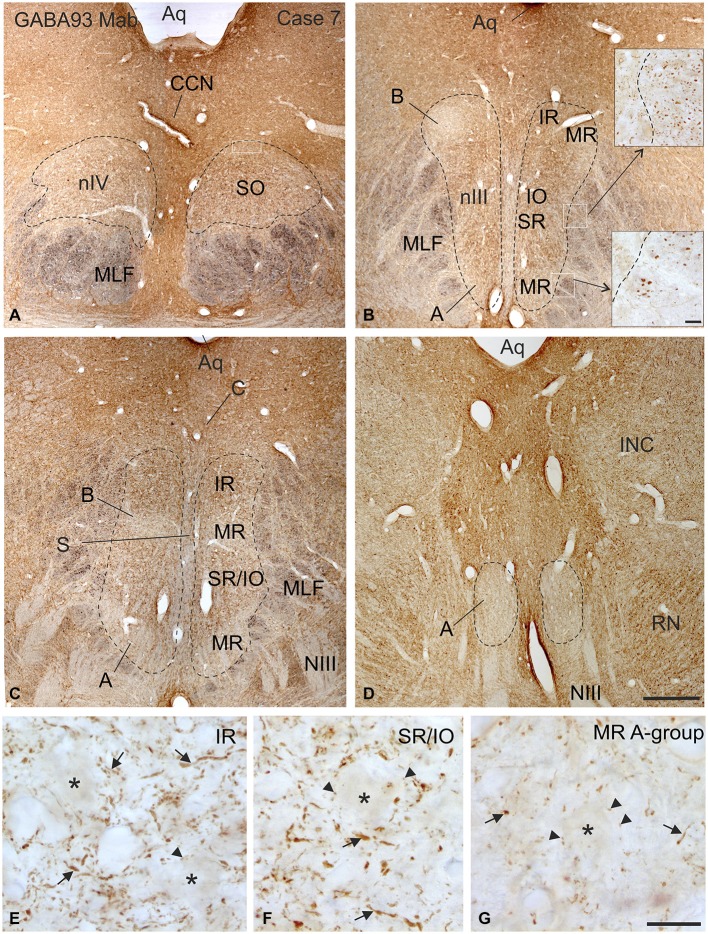
Figure 2.
Overview of coronal sections through the oculomotor (nIII) and trochlear nucleus (nIV) in monkey to demonstrate the immunostaining for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). A dense labeling of GABA-positive terminals is found in nIV. (A) All subgroups in nIII express a similar strong GABA-immunoreactivity, except the MR A and B-group, where a weaker labeling is observed (B–D). Note numerous GABAergic fibers are present in the medial longitional fascicle (MLF) next to the middle part of nIII containing motoneurons of vertically pulling eye muscles (B, upper inset), whereas much fewer GABA-positive fibers are found within the MLF portion adjacent to the MR A-group (B, lower inset). Detailed views of motoneuronal groups for vertical (E,F) and horizontal eye movements (G) reveal that most GABA immunoreactive profiles represent traversing fibers and cut axons (arrows) and only weakly stained puncta may form terminals (arrow heads) around motoneuronal somata (E–G, asterisks). Aq, aqueduct; CCN, central caudal nucleus, NIII, oculomotor nerve; INC, interstitial nucleus of Cajal; IO, inferior oblique muscle; RN, red nucleus; SR, superior rectus muscle; MIF, multiply innervated muscle fibers. Scale bar = 500 μm in (D) (applies to A–D); 30 μm in inset of (B); scale bar = 30 μm in (G) (applies to E–G).