Figure 1.
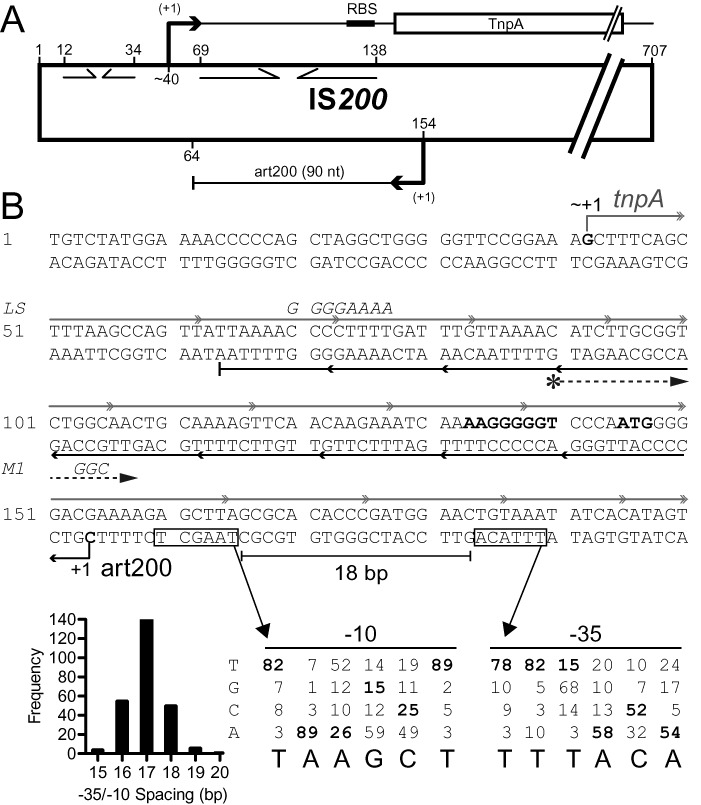
Schematic of IS200. (A) IS200 is 707 basepairs in length. It contains a single protein coding gene (transposase; tnpA), transcription of which originates at about nt 40 (23,35); tnpA promoter elements have not been defined. The ‘left end’ contains two internal inverted repeats (opposing arrows), one of which acts as a transcription terminator (nts 12–34) and the other (nts 69–138) was predicted to encode a stem-loop structure in the 5'UTR of the tnpA mRNA that sequesters the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (35). IS200 in Salmonella also expresses a 90 nt sRNA (art200, previously STnc490), which is perfectly complementary to the 5'UTR and the first three codons of tnpA. The transcription start site and 3’ end for art200 in Salmonella (derived from RNA-Seq experiments) are shown but promoter elements were not previously defined (19). (B) The DNA sequence of the first 200 nucleotides of IS200 is shown. The tnpA and art200 transcripts are shown in gray and black, respectively. Putative promoter elements for art200 are boxed and the Salmonella transcription start site (+1) is shown. The former were predicted using a position weight matrix (showing nucleotide identity of −10 and −35 promoter elements for E. coli) and the optimal spacing between −10 and −35 elements in E. coli (histogram) (data from (41)). The SD sequence and start codon for tnpA are shown in bold. Mutations introduced into tnpA/art200 in this work (LS and M1) are indicated in italics. A DNA primer used to map the 5' end of art200 in E. coli (Figure 2) is depicted with an asterisk followed by a dashed arrow.
