Fig. 1.
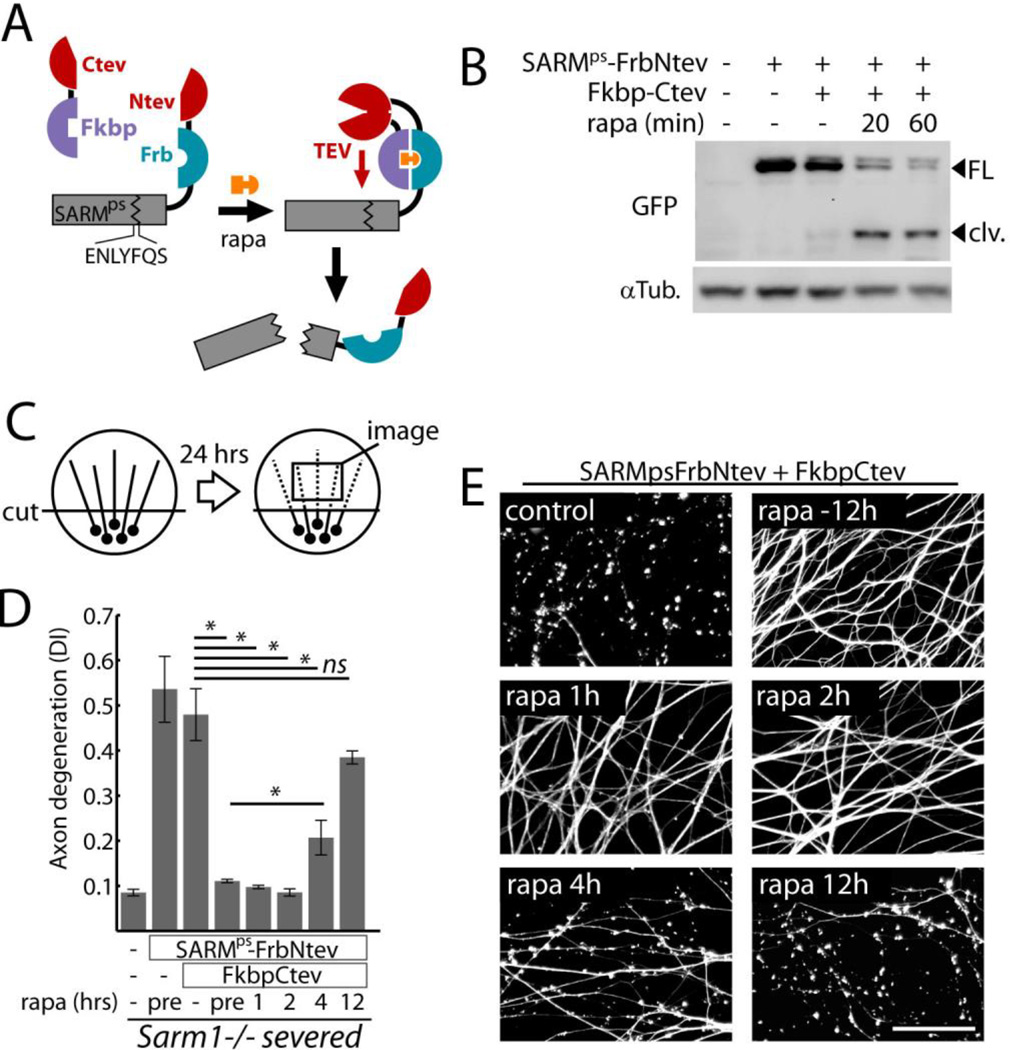
SARM1 functions following axon injury to promote destruction. A) Schematic showing how expression of SARMps-Frb-Ntev with Fkbp-Ctev allows rapamycin-induced complementation of split TEV and concomitant SARMps cleavage. B) Gel electrophoresis with anti-GFP immunoblot showing SARMps cleavage in DRG neurons induced by 100 nM rapamycin (rapa); FL=full length SARMps-Frb-Ntev-Cerulean; clv = cleaved form. α-Tubulin (αTub) was a loading control. C) Diagram of in vitro injury model: isolated DRG neurons were severed and axon degeneration was quantified after 24 hours from axon images. D) Requirement for SARM1 activity after axotomy to induce axon degeneration.. Axon degeneration is reported as the degeneration index (DI), a morphometric ratio of fragmented axon area to total axon area (13). Sarm1−/− DRG neurons treated with expression lentiviruses (control, SARMps-FrbNtev, and Fkbp-Ctev) were severed and treated with 100 nM rapamycin at various times (pre = 12 hours pre-injury). E) Micrographs show representative α-Tubulin stained axons corresponding to select treatment groups in (D). Scale bar = 50 micrometers. Error bars = SEM; * p < 0.01; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post-hoc test.