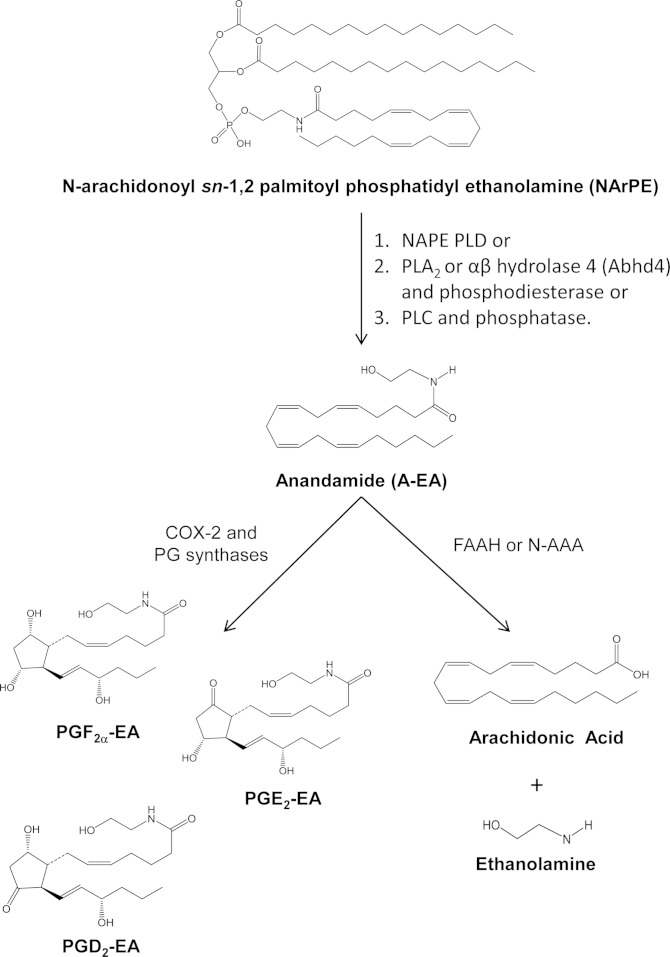
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of prostamide biosynthesis. A-EA is released from NArPE by the action of NAPE-PLD (1), PLA2 or αβ hydrolase 4 (abhd4) and a metal dependent phosphodiesterase (2), or PLC and phosphatases (3) [e.g., tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22)]. Subsequently, A-EA is metabolized by COX-2 and PGSs to prostamides such as PGE2-EA, PGD2-EA, and PGF2α-EA. A-EA can also be hydrolyzed by FAAH or N-AAA to arachidonic acid and ethanolamine.