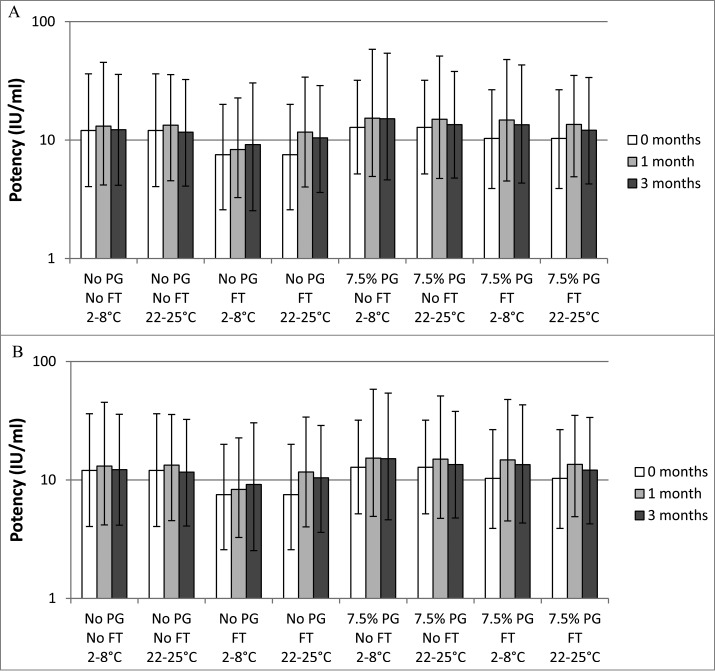
Figure 1.
In vivo potency of whole cell pertussis (Fig. 1A) and acellular pertussis (Fig. 1B) components of vaccines formulated with or without 7.5% (v/v) PG. The vaccines were exposed to freeze-thaw treatment (FT) or not (no FT) and stored at the indicated temperature for 0, 1, or 3 months before being used to immunize mice to test for their ability to protect against intracerebral challenge. IU: international units; FT: freeze-thaw; PG: propylene glycol. The error bars represent the upper and lower 95% confidence intervals. Potencies of acellular pertussis and whole cell pertussis vaccines were determined using the modified intracerebral challenge assay.9 NIH/OlaHsd mice were immunized intraperitoneally with 0.5 mL of serial dilutions of test vaccines or acellular pertussis reference vaccine. After 21 days, the mice were challenged by intracerebral injection of 100 to 1,000 LD50 of Bordetella pertussis organisms and observed daily for 14 d for paralysis and death. The number of surviving animals was recorded. Mice that died within 72 hours of the challenge were excluded from the analysis. The percentage of animals surviving at each dilution was used to calculate the potency compared with the international standard using the Reed-Muench equation and converted to potency IU per mL.