Figure 4.
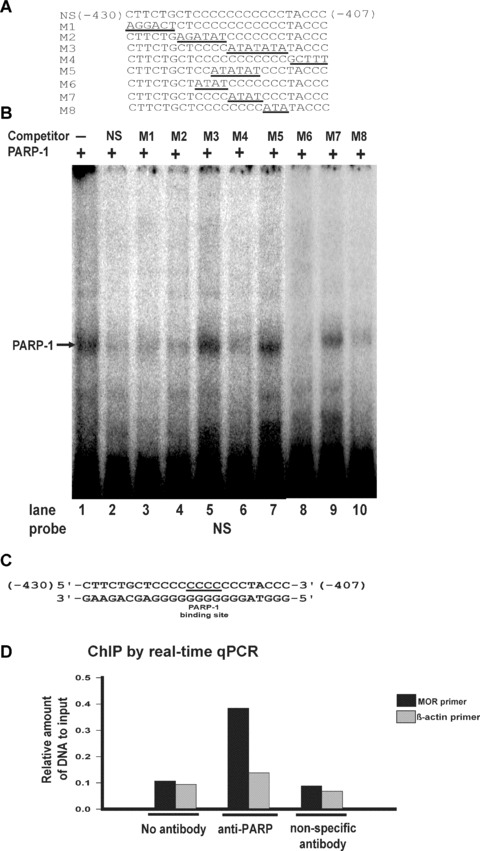
EMSA analysis of the PARP-1-binding motif using mutant oligonucleotide sequences and ChIP assay. (A) Representation of the double-stranded oligonucleotide sequence (NS) and mutant oligonucleotide sequences (M1–M8). (B) EMSAs were performed using unlabelled poly(C) sequence (NS; lane 2) or unlabelled poly(C) mutated sequences (M1–M8; lanes 3–10) as competitors for recombinant PARP-1 protein binding to a labelled poly(C) sequence. Lane 1: Negative control (no unlabelled poly(C) sequence). The PARP-1-poly(C) sequence complex is indicated by an arrow. (C) The PARP-1-binding motif of the poly(C) sequence (NS). (D) ChIP analysis by real-time qPCR for PARP-1 binding interaction with the MOR promoter poly(C) sequence. Interactions were examined by ChIP assay with anti-PARP antibody and nonspecific antibody (anti-gal4). Precipitated DNAs were amplified using mouse MOR and β-actin (negative control) primers.
