Figure 7.
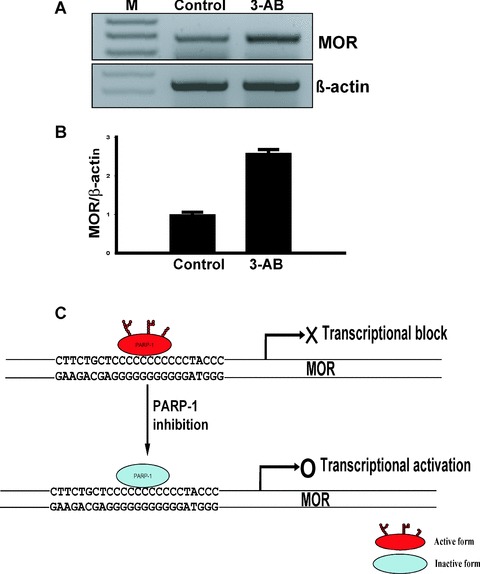
3-AB inhibits mouse MOR mRNA expression in NS20Y cells and schematic model for PARP-1 in modulation of mouse MOR transcription. (A) Quantification of transcripts was performed by RT-PCR. Total RNA from NS20Y cells treated with 2 mM 3-AB was prepared and treated with DNase I. Primer pairs specific for the coding sequence of each gene were used for RT-PCR. PCR products were visualized in a 2% agarose gel. Lane 1: Molecular weight markers (M); lane 2: Control; lane 3: 3-AB-treated cells. (B) Quantitative analysis using ImageQuant 5.2 software. The MOR mRNA levels from Control and 3-AB-treated cells were normalized against β-actin levels. The values were obtained from triplicate data points. Changes in transcript levels for 3-AB-treated samples were compared to Control, which was assigned a value of 1.0. Bars indicate the range of standard error. (C) Schematic model for the role of PARP-1 in modulation of mouse MOR gene transcription. In neuronal cells, enzymatically active PARP-1 interacts strongly with the poly(C) sequence of the mouse MOR promoter and aids in the formation of tran-scriptionally inactive chromatin. Enzymatic inhibition of PARP-1 by 3-AB results in non-poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated PARP-1 and subsequently, an increase in the levels of MOR mRNA in mouse NS20Y cells.
