Figure 5.
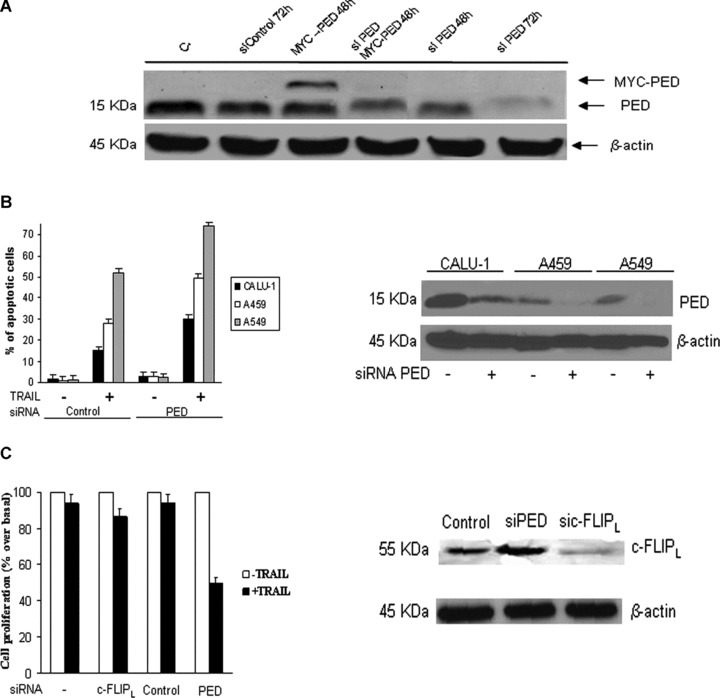
Down-regulation of PED restores TRAIL sensitivity in CALU-1 cells. (A) PED siRNA or a control oligo were transiently transfected in CALU-1 cells in the presence or absence of PED-Myc cDNA. Cells were incubated for 48 or 72 hrs and analysed by Western blotting. The PED siRNA duplex suppressed both exogenous and endogenous PED expression, whereas control siRNA had no effects. (B) PED siRNA effects in A459 and A549 cells. PEDsi RNA, transfected in NSCLC cells was able to reduce PED expression levels (right panel) and induce an increase in TRAIL sensitivity (left panel), as assessed by flow cytometry. Mean ± SD of two independent experiments in duplicate. (C) c-FLIPL siRNA or PED siRNA were transfected as described in Methods. Cells were analysed for c-FLIP expression after 72 hrs incubation. c-FLIPL siRNA but not PED siRNA was able to reduce c-FLIPL expression Effects of silencing PED and c-FLIPL on TRAIL-induced cell death: CALU-1 cells were transfected with siRNA for PED, c-FLIPL or control for 48 hrs, after which cells were trypsinized, plated in 96-well plates in triplicate and further incubated with superkiller TRAIL for 24 hrs. Metabolically active cells were then detected as indicated in the Methods. Mean ± SD of four independent experiments in duplicate. Down-regulation of PED, but not cFLIPL, was responsible for increased sensitivity of CALU-1 cells to TRAIL-mediated cell death.
