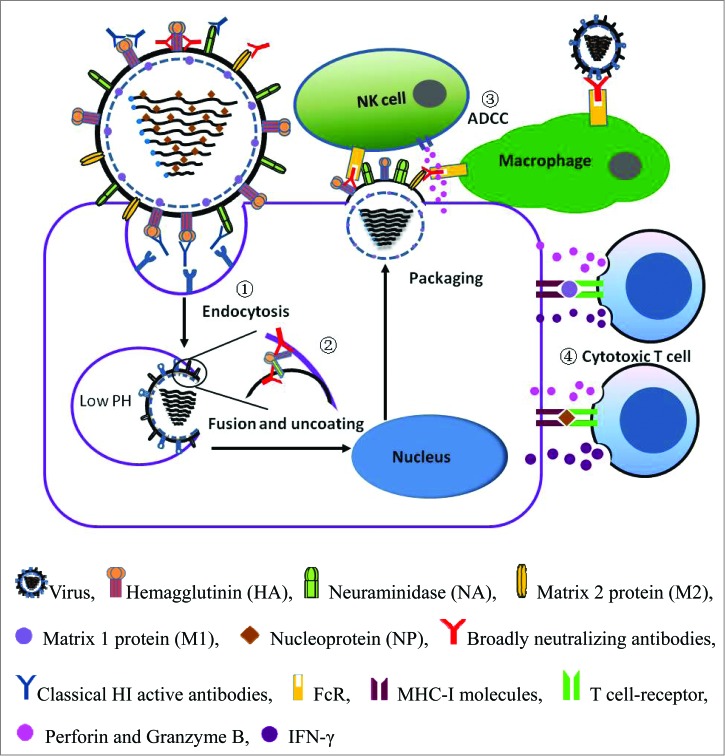
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of influenza virus infection and the adaptive immune responses involved in host defense. (1) Classical HI antibodies prevent receptor-mediated endocytosis of the virus by binding to the HA head domains, which are typically variable. (2) Broadly neutralizing antibodies prevent membrane fusion by binding to the highly conserved HA stem. (3) Broadly neutralizing antibodies specific for HA stem and viral internal proteins mediate ADCC of infected cells, which is dependent on binding to FcR. (4) The influenza A virus internal proteins, M1 and NA, induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific responses, which are dependent on MHC-I molecules.