Fig. 2. Effect of C(-1019)G polymorphism rs6295 on 5-HT1A receptor expression.
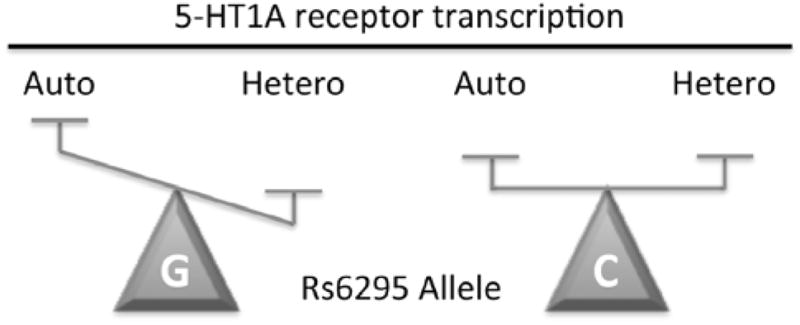
A simplistic model of the C(-1019)G change (labeled C or G), which prevents Deaf1 from recognizing its element on the 5-HT1A promoter, is presented. In 5-HT neuronal cells, Deaf1 represses 5-HT1A receptor transcription, but in certain non-serotonergic neurons it oppositely enhances 5-HT1A expression. An upregulation of 5-HT1A autoreceptor (Auto) expression in raphe neurons is predicted for the G(-1019) allele based on loss of Deaf1-mediated repression presynaptically. Conversely, in some non-serotonergic neurons a reduction in 5-HT1A heteroreceptor (Hetero) expression is predicted based on the loss of Deaf1 enhancer activity.
