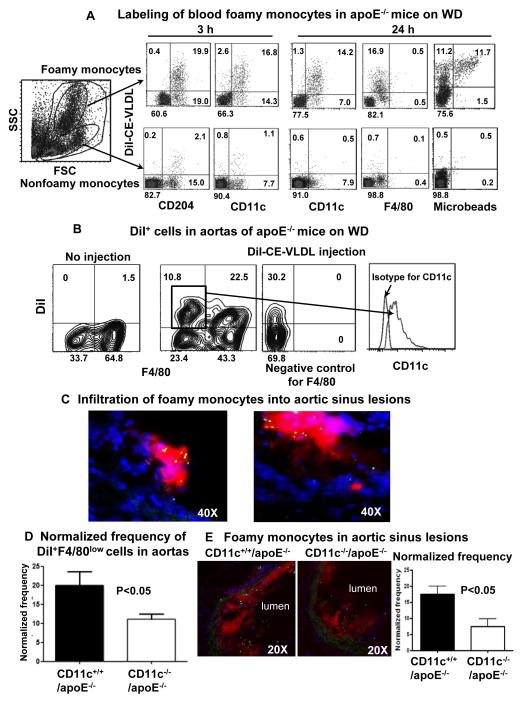
Figure 5. Labeling of foamy monocytes and infiltration of foamy monocytes into nascent atherosclerotic lesions.
A, Representative flow cytometric analysis samples showing specific labeling of foamy monocytes and phenotypes of labeled foamy monocytes in apoE−/− mice on WD (3 weeks) after intravenous injection of DiI-CE-VLDLs with or without fluorescent microbeads, from more than 5 independent experiments with at least 3 samples in each experiment. B, Representative flow cytometric analysis samples showing foamy monocytes (DiI+F4/80low) in atherosclerotic aortas with sustained expression of CD11c, from 4 independent experiments with at least 3 samples in each experiment. C, Representative histology of aortic sinus showing accumulation of microbead+ (green) cells, which were also DiI+ (red, left panel) and CD11c+ (red, right panel), in atherosclerotic lesions of apoE−/− mice on WD (3 weeks) after intravenous injection of fluorescent microbeads with (left panel) or without (right panel) DiI-CE-VLDLs. D, Normalized frequency of infiltrated foamy monocytes in aortas of CD11c−/−/apoE−/− and CD11c+/+/apoE−/− mice on WD (3 weeks). n=5–7 samples/group. E, Representative histology and quantification of foamy monocyte infiltration in aortic sinus lesions of CD11c−/−/apoE−/− and CD11c+/+/apoE−/− mice on WD (3 weeks). n=15 samples/group.