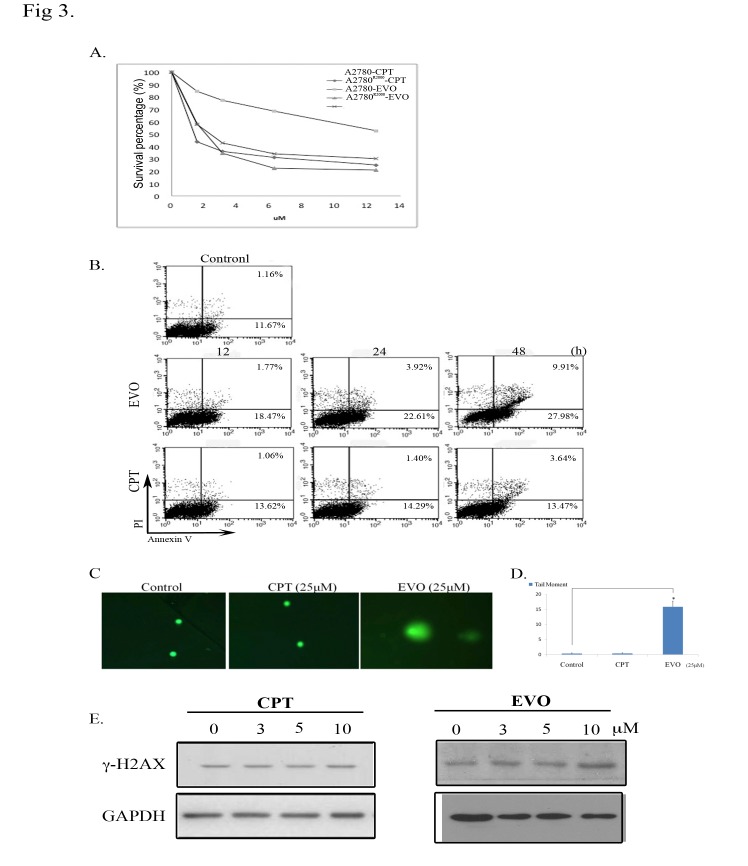
Fig 3. Evodiamine (EVO) exerted a cytotoxic effect on A2780R2000 cells.
(A) The viability of A2780 and A2780R2000 cells was assessed after 48 h of treatment with camptothecin (CPT) or EVO using an MTT assay, and IC50 values were determined. (B) FITC/PI flow cytometry of A2780R2000 cells treated with EVO (10 μM) for 12–48 h compared with cells treated with CPT (10 μM) for 12-48h. (C). EVO-induced DNA damage in A2780R2000 cells. Cells were untreated or treated with CPT and EVO (25 μM) for 1 h and were then analyzed using a neutral comet assay, as described in the Materials and Methods section. Representative images (200×). (D) Histogram of the tail moment plotted against each treatment condition. p values of comparisons (marked with *) were <0.05 as determined using a 2-tailed Student’s t test. (E) γ-H2A.X levels after EVO or CPT treatment in A2780R2000 cells. Cells were treated (0–10 μM) for 6 h, and cell lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody against γ-H2A.X. GAPDH with constant expression was used as the internal control.