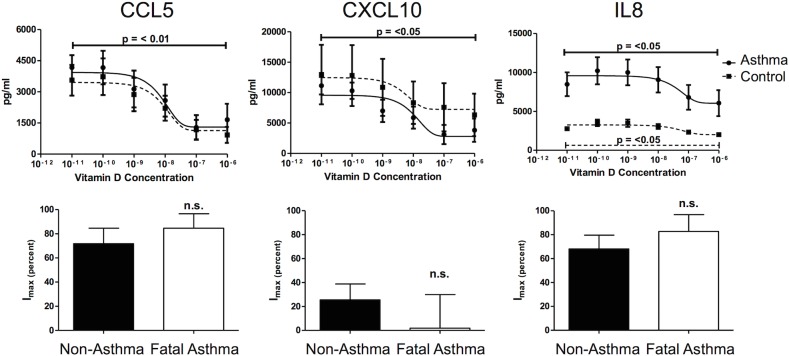
Fig 4. Vitamin D inhibited TNFα-induced cytokine expression.
Although the amount of inhibition differed by cytokine, vitamin D inhibited three cytokine levels to a comparable degree in fatal asthma-derived vs. non-asthma-derived ASM, even for IL8, whose TNFα-induced baseline secretion was significantly higher in fatal asthma- vs. non-asthma-derived ASM. Data represent means ± standard error of the mean for ASM cells derived from 5 fatal asthma donors and 10 non-asthma donors. Each condition was measured in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s two-tailed t-test with a p<0.05 threshold. Bottom panels compare baseline TNFα-induced cytokine levels to those obtained with a maximal inhibitory vitamin D concentration (Imax).