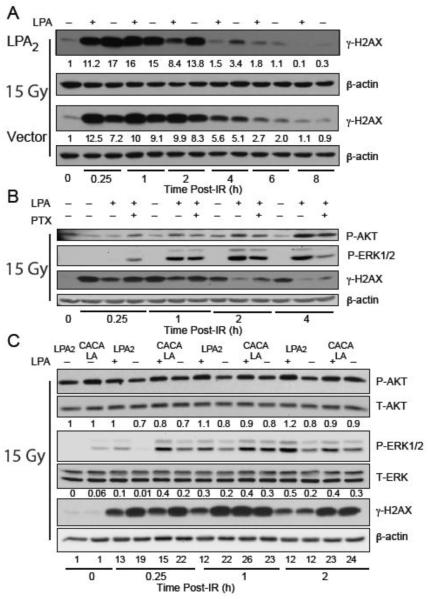
Figure 3. LPA2 facilitates the radiation induced DNA damage repair in part via the classical G-protein-coupled signals and also the ternary macromolecular complex between LPA2-TRIP6-NHERF2 indicated by γH2AX levels detected by Western blotting.
Panel A. Time-course of γH2AX resolution in LPA2-MEF (LPA2) and Vector MEF preincubated with 10 μM LPA and irradiated with 15 Gy confirms the role of LPA2 in DNA damage repair with a 10 × higher residual γH2AX expression level in Vector MEF 8 h post-IR treatment. Panel B. Inhibition of Gi/0 heterotrimeric G proteins with PTX in LPA2-MEFs prior to irradiation treatment (15 Gy) results in reduced AKT and ERK1&2 activation and accumulation of γH2AX. Panel C. Disruption of the ternary macromolecular signaling complex formed between LPA2-TRIP6-NHERF2 in the CACALA-MEFs pretreated for 15 minutes with either 10 μM LPA or vehicle and irradiated with 15 Gy results in reduced AKT and ERK1&2 activation and a subsequent γH2AX accumulation. Arbitrary units represent light intensity values measured by Image J software and normalized to β-actin and calculated as fold over non-irradiated control.