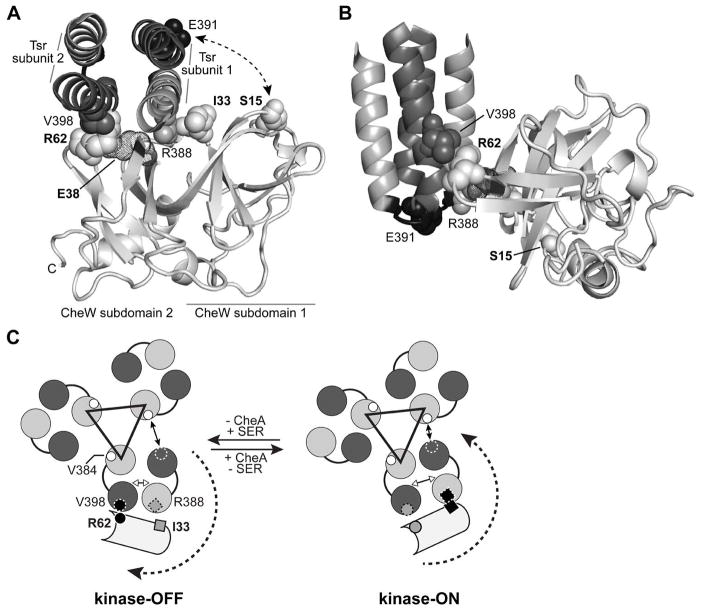
Fig. 5. CheW-Tsr contacts during signalling.
(A) Interaction of the E. coli CheW protein (light grey) with the Tsr N-helix (grey) and C-helix (dark grey) at the hairpin tip. The docked structure was modelled from the atomic coordinates for the corresponding Thermotoga protein complex (PDB 3UR1, Briegel et al., 2012). Only residues 373–409 of Tsr are shown, viewed in the membrane-proximal to -distal direction. Residues that formed disulphide crosslinks in the present work are shown space-filled. CheW residue E38, which is thought to form a salt bridge with CheW-R62 (Ortega et al., 2013b), is shown in dot representation.
(B) Side view of the modelled CheW-Tsr complex. The structure shown in (A) was rotated 90° about the X and Y axes to show the juxtaposition of the Tsr-V398 (dark grey) and CheW-R62 (light grey) side chain atoms. The loop that joins the N- and C-helices of Tsr is shaded black; residue E391 (space-filled) defines its mid-point.
(C) Model of the signalling-related motions of CheW interacting with the Tsr trimer of dimers. The Tsr N- and C-helices are depicted as grey and dark grey circles. The black triangle connects the N-helices of the inner subunits at the trimer axis that make most of the trimer-stabilizing contacts between receptor dimers. A CheW molecule (light grey) is shown interacting with the outer helices of one Tsr dimer. CheW-R62C (small circle) crosslinks most efficiently with Tsr-V398C (small circle with dashed circumference) in the kinase-OFF signalling state (black circles, left). CheW-I33C (small square) crosslinks most efficiently with Tsr-R388C (small square with dashed border) in the kinase-ON signalling state (black squares, right). The receptor molecules are thought to undergo conformational shifts during signalling that rotate the C-helix of the outer subunit of one dimer toward or away from the N-helix of the inner subunit of the neighbouring dimer. In consequence, the interaction between V398 in the C-helix of the outer subunit (small dashed circle outline) changes its distance relative to V384 in the N-helix of the inner subunit (small white circles). The distances between helices in the trimer of dimers are based on the molecular dynamics study done by Ortega et al 2013a (Fig. 5 in cited reference).