Figure 3.
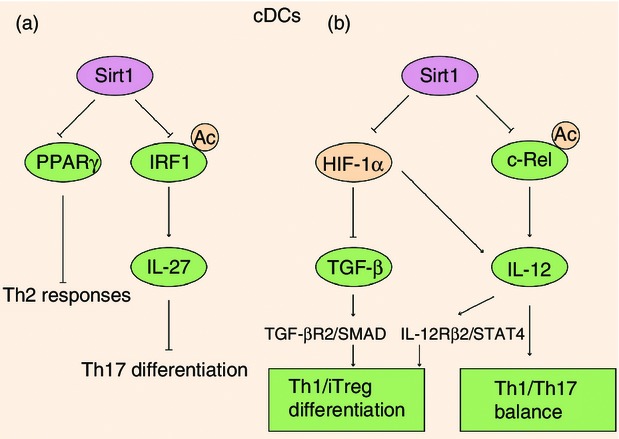
Sirt1 regulated the immune responses in dendritic cells (DCs). (a) Sirt1 inhibition disables conventional DCs to prime T helper type 2 (Th2) responses in the airways by depressing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ). On the other hand, Sirt1 deacetylates interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) to suppress IRF1 binding to the promoter region of the p28 subunit of interleukin-27 (IL-27), modulating Th17 differentiation during MOG-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. (b) Sirt1-HIF-1α signalling axis is required for DCs to guide the Th1 and iTreg cell differentiation through regulating the expression of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-12. Moreover, Sirt1 modulates the IL-12 p70/IL-23 balance in response to phagocytic stimuli by deacetylating histone and reducing the accessibility of c-Rel to the il12a promoter and its transcriptional activation.
