Figure 1.
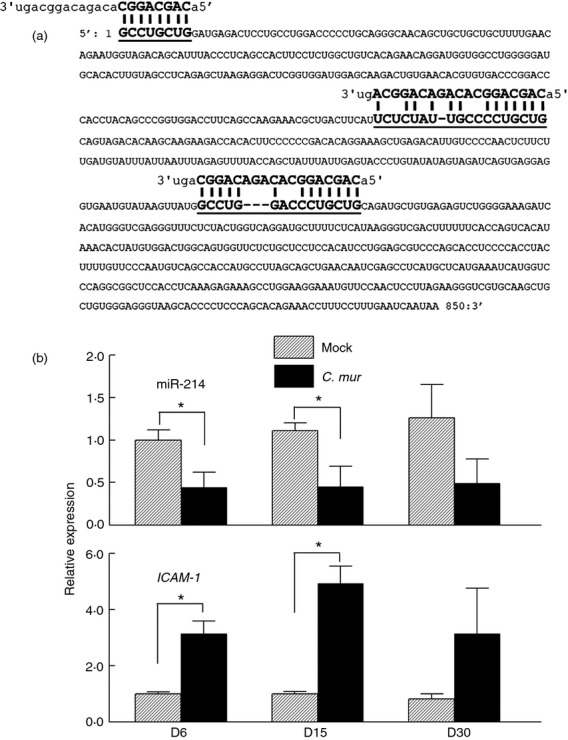
Increased intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1) gene expression is correlated with down-regulation of microRNA-214 (miR-214) in Chlamydia muridarum-infected mice. (a) Bioinformatic analysis using algorithms by www.microRNA.org and www.targetscan.org revealed miR-214 putative binding sites in the ICAM1 gene. (b) C57BL/6 (wild-type; WT) mice were challenged intravaginally with 5 × 104 inclusion-forming units (IFU) or treated with sucrose/phosphate/glutamate buffer (mock). Genital tract tissue was excised at days 6, 15 and 30 post challenge. RNA was extracted, converted to cDNA, and real-time PCR was performed to determine relative miR-214 and ICAM1 mRNA levels to D6 mock control. *P < 0·05 (Student's t-test) for C. muridarum-infected group compared with mock group. Data are representative of two individual experiments.
