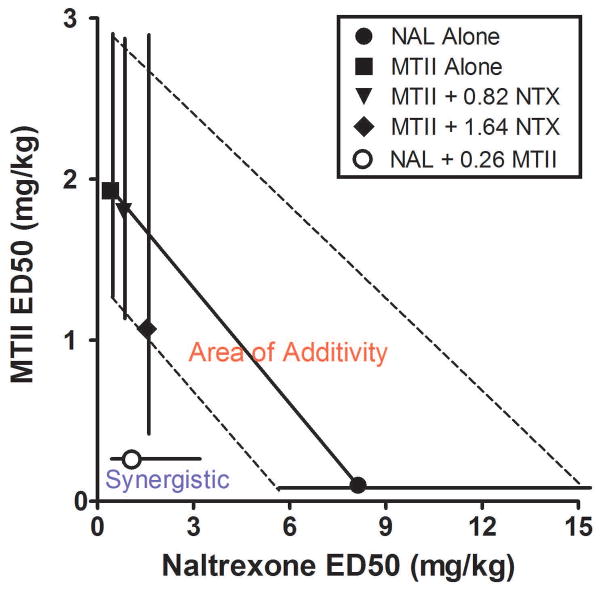
Fig. 4.
Isobolographic analysis of the effects of NAL and MTII administered in selected combinations. For this analysis, the ED50 and 95% confidence levels (C.L.) for the effects of NAL (solid circle) and MTII (solid square) alone on binge-like ethanol drinking were plotted along the abscissa and ordinate, respectively. Then the ED50 and 95% C.L. for drugs when tested in combination with the ED20 or ED30 of the other drug were plotted. The area between dashed lines that connect the 95% C.L. of the ED50 for each drug alone represents the “area of additivity”, the area in which drug interactions were considered to be additive. The region to the left of the dashed line defines synergistic drug interactions. The data show that the low ED20 dose of MTII (0.26 mg/kg) synergistically augmented the ability of NAL to blunt binge-like ethanol drinking, shifting the dose-response ED50 value of NAL to the left beyond the area of additivity and into the region representing synergistic drug interactions. Neither the low ED20 (0.82 mg/kg) nor high ED30 (1.64 mg/kg) doses of NAL synergistically altered the ED50 values for MTII-induced blunting of binge-like ethanol drinking, as the ED50 for these drug dose combinations fell within the area of additivity.