Fig 2.
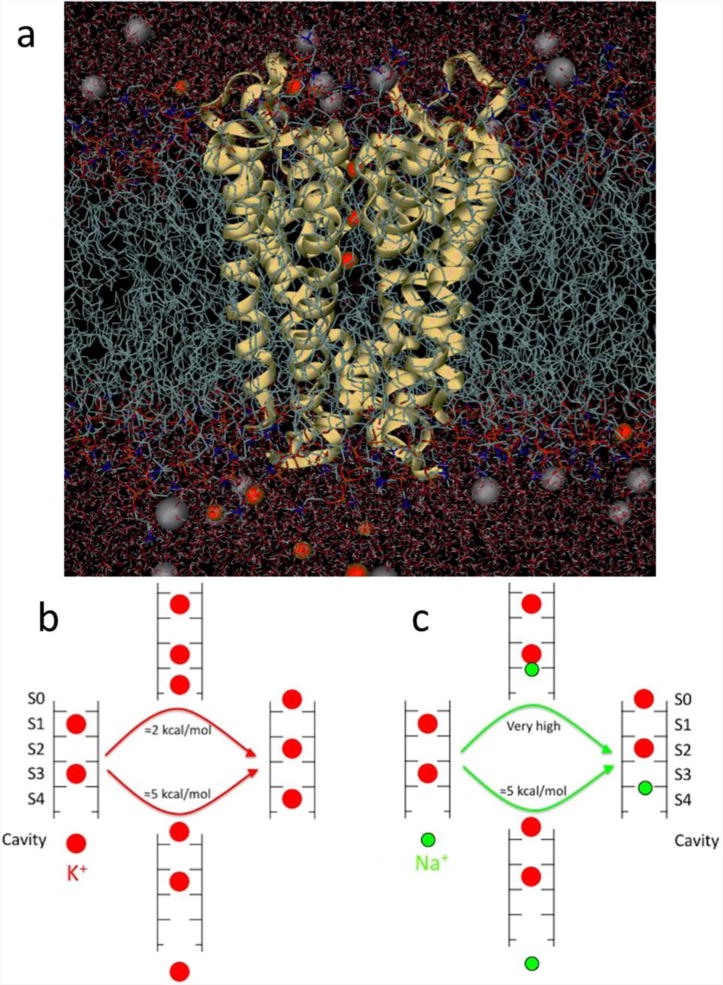
(a) Fully atomistic KcsA ion channel system (protein as yellow ribbons, lipid tails as chains, water as sticks and K+ and Cl− ions as red and grey balls, respectively). (b) Differing multi-ion barriers for K+ and Na+. The low barrier to K+ outward conduction results from the ability of a K+ ion (red) to bind to the entrance of the selectivity filter. (c) The shift of binding site for Na+ (green), eliminates this process and requires a substantial amount of energy. Based on (Nimigean & Allen, 2011).
