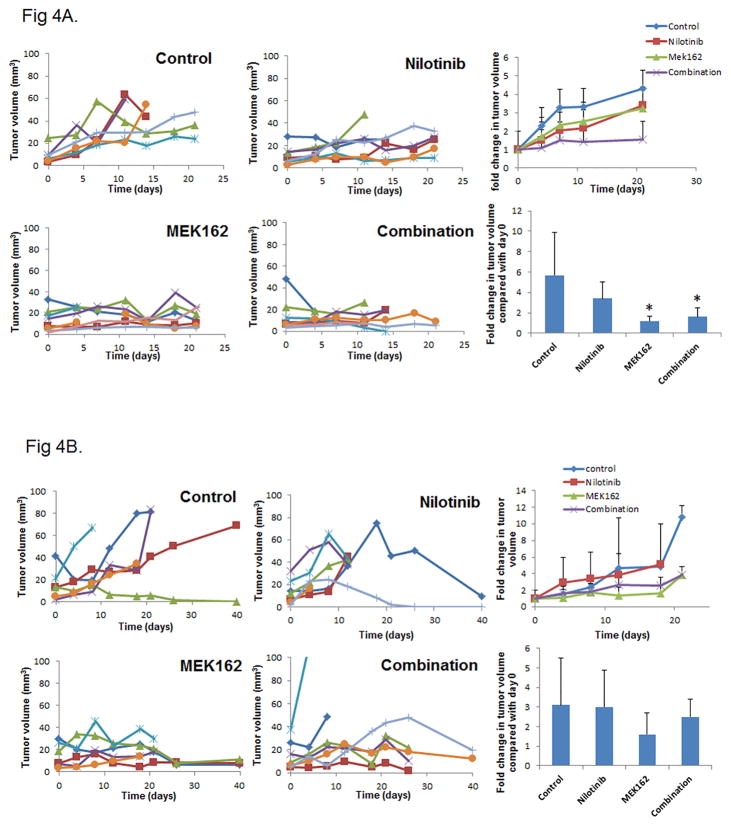
Figure 4.
Nilotinib does not enhance MEK162 inhibition of tumor growth in an orthotopic mouse model. Mice were injected with UMSCC47 cells in the tongue. After 2 weeks, tumor-bearing mice were grouped randomly and treated with nilotinib only, MEK162 only, a combination of nilotinib and MEK162, or vehicle only for 7 days per week (A) or 4 days per week (B). Tumor volume was measured periodically and plotted against time for the mice individually with each color representing an individual mouse (left 4 graphs). The average fold change in tumor volume over time (upper right) and at day 21 or at the time of euthanasia (lower right) was compared with day 0 (treatment start date). Error bars indicate standard deviation. *p < 0.05 compared with untreated control.