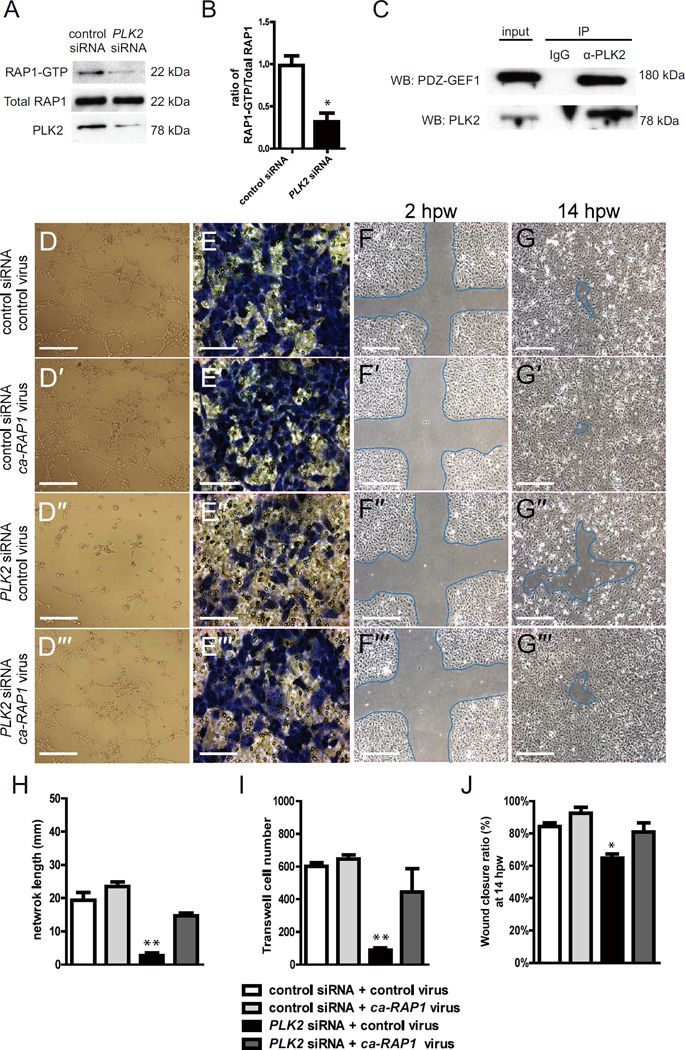
Figure 5. PLK2 regulates HUVEC migration in vitro via RAP1 activity.
(A) RAP1 immunoblot of RAP1-GTP binding assays shows that there is less RAP1-GTP in PLK2 siRNA HUVECs than in control siRNA HUVECs (22 kDa). PLK2 immunoblot shows the efficiency of PLK2 siRNA knockdown in HUVECs. (B) Quantitative measurements shows that the ratio of RAP1-GTP/Total RAP1 is less in PLK2 siRNA (Mean +/− s.e.m. *p = 0.015 by Student's t-test). (C) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of HUVEC lysates with anti-PLK2 antibody reveals that PLK2 interacts in a complex with PDZ-GEF1 (180 kDa). Western analyses of immunoprecipitations were performed with anti-PDZ-GEF (WB: PDZ-GEF) and anti-PLK2 antibodies (WB: PLK2). IP IgG – control antibody; α-PLK2 – anti-PLK2 antibody. (D) EC tube formation assays, (E) Transwell EC migration assays, and (F, G) wound healing EC assays show that ca-RAP1 virus can rescue the PLK2 siRNA knockdown HUVEC (compare D” to D”’) EC network/tube formation, (compare E” to E”’) cell migration, and (compare F”, G” to F”’, G”’) wound healing defects. (D-D”’, F-F”’, G-G”’) Scale bar, 1.6 mm. (E-E”’) Scale bar, 400 µm. (H–J) Quantitative measurements were performed on (H) EC tube formation assays, (I) transwell EC migration assays, and (J) wound healing EC assays. hpw - hours post wounding. Mean +/− s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by ANOVA for H–J.