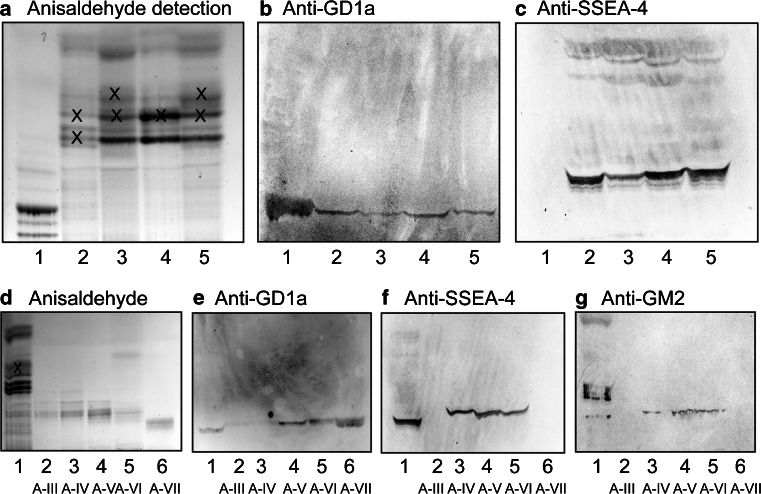
Fig. 8.
Binding of monoclonal antibodies to the acid glycosphingolipids from moose small and large intestine. Thin-layer chromatogram after detection with anisaldehyde (a and d), and autoradiograms obtained by binding of antibodies directed against the GD1a ganglioside (b and e), the sialyl-globopenta/SSEA-4 determinant (c and f) and the GM2 ganglioside (g). The glycosphingolipids were separated on aluminum-backed silica gel plates, using chloroform/methanol/water 60:35:8 (by volume) as solvent system, and the binding assays were performed as described under “Materials and methods”. Autoradiography was for 12 h. The lanes on a–c were: Lane 1, calf brain gangliosides, 40 μg; Lane 2, total acid glycosphingolipids of moose I small intestine, 40 μg; Lane 3, total acid glycosphingolipids of moose II small intestine, 40 μg; Lane 4, total acid glycosphingolipids of moose III small intestine, 40 μg; Lane 5, total acid glycosphingolipids of moose I large intestine, 40 μg. The lanes on d–g were: Lane 1, total acid glycosphingolipids of moose I small intestine, 40 μg; Lanes 2–6, fractions A-III – A-VII, 4 μg/lane. The bands marked with X on (a) and (d) are non-glycosphingolipid contaminants