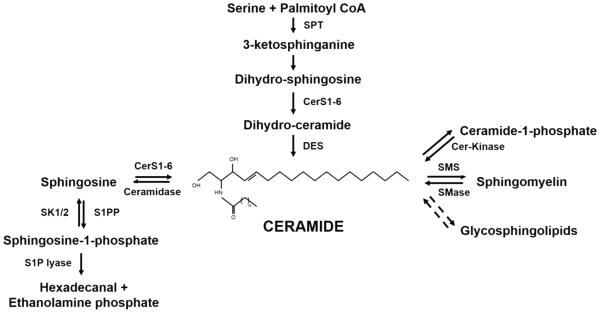
Fig. 1.
Ceramide metabolic pathways. Ceramide lies at the center of sphingolipid metabolism. Ceramide de novo generation starts with a condensation reaction involving Serine and Palmitoyl CoA by the enzyme Serine Palmitoyl CoA Transferase (SPT), to generate 3-ketosphinganine, which is then converted to sphinganine or dihydrosphingosine. Then, Ceramide Synthases (CerS1-6) transfer a fatty acyl CoA to the amino group yielding dihydroceramide which gets desaturated to ceramide by Dihydro-ceramide Desaturase enzyme (DES). Ceramide can be generated back from Sphingosine-1-phosphate with the help of S1P phosphatase (S1PP) and ceramide synthase (salvage pathway) or from Sphingomyelin by Sphingomyelinase (SMase), from Glycosphingolipids, or from Ceramide-1-phosphate by Ceramide kinase (Cer-Kinase). As a metabolic outlet for ceramide, it is converted to sphingosine by the action of ceramidase. Sphingosine kinases 1 and 2 (SK1/2) phosphorylate sphingosine to sphingosine-1-phosphate that can be further degraded by S1P lyase to hexadecanal and ethanolamine phosphate.