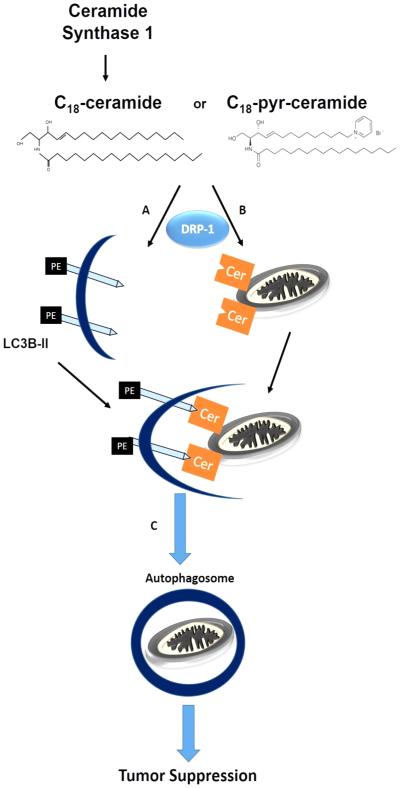
Fig. 3.
Regulation of mitophagy by ceramide. Endogenous generation of C18-ceramide via CerS1 or exogenous treatment by C18-pyridinium-ceramide is followed by two processes: A. conjugation of LC3-I to phosphatidylethanolamine on the carboxy terminal to form LC3-II and B. accumulation of ceramide in the mitochondrial outer membrane. Ceramide in the mitochondrial membrane acts as a receptor to LC3-II by binding to its amino terminal, opposite to where PE is conjugated. This results in C. recruiting the autophagosome to engulf the mitochondria. Lysosomes then fuse with the autophagosomes (D) for hydrolytic degradation of the contents.