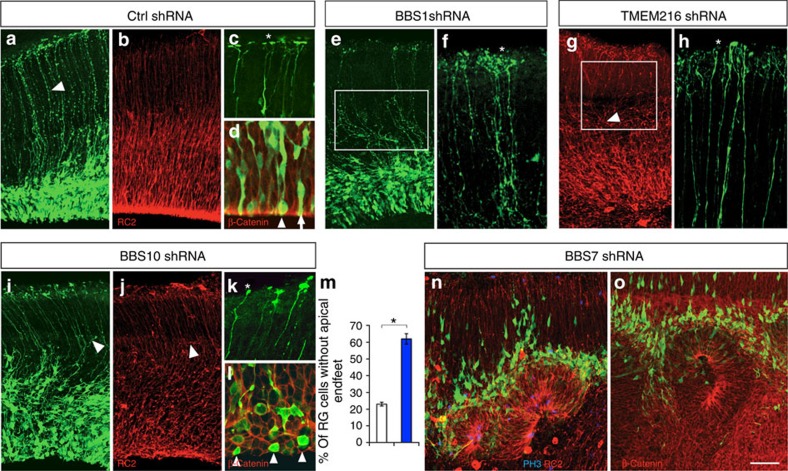
Figure 2. Ciliopathy-related gene effects on polarized radial glial progenitor morphology.
(a–d) Control radial glial (RG) progenitor scaffold. Polarized RG are labelled with anti-GFP (a) and anti-RC2 (b). The basal processes of control radial glia (a, arrowhead) spanning the entire width of the developing embryonic cerebral cortices were labelled with electroporated GFP. (c) Higher-magnification view of basal endfeet (adjacent to asterisk) labelled with GFP. (d) Higher-magnification view of GFP+ radial glial cell bodies in VZ and apically enriched β-catenin (red) lining the ventricular surface. Radial glial cell soma is localized either adjacent to the ventricular surface (arrowhead) or just above with elongated apical endfeet (arrow). (e,f) BBS1 shRNA knockdown results in RG with wavy basal processes (square; e) and disrupted basal endfeet (see endfeet adjacent to asterisk; f). (g,h) TMEM216-deficient radial glia do not fasciculate as densely as in controls (square; g) and are often shorter and misoriented (arrowhead; g). (h) Disrupted basal endfeet in TMEM216 shRNA-expressing RG cells (see endfeet adjacent to asterisk). (i–m) Knockdown of BBS10 lead to aberrantly branched, short or retracted (arrowhead; f,i) RG scaffold. (k) Enlarged view of GFP+-expressing BBS10 shRNA basal endfeet illustrates the unbranched morphology of basal endfeet (see endfeet adjacent to asterisk). (l) BBS10 shRNA expression results in loss of apical endfeet, and apical enrichment of β-catenin (red). (m) Quantification of percentage BBS10 shRNA-expressing RG without apical endfeet. Number of cells: 134 (control); 189 (BBS10). (n,o) BBS7 shRNA expression results in rosette-like organization of the ventricular zone and aberrant β-catenin expression. Data shown are mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). Number of brains per group=4. Scale bar, 20 μm (a,b,e,g,i,j,n,o); 5 μm (c,d,f,h,k,l).