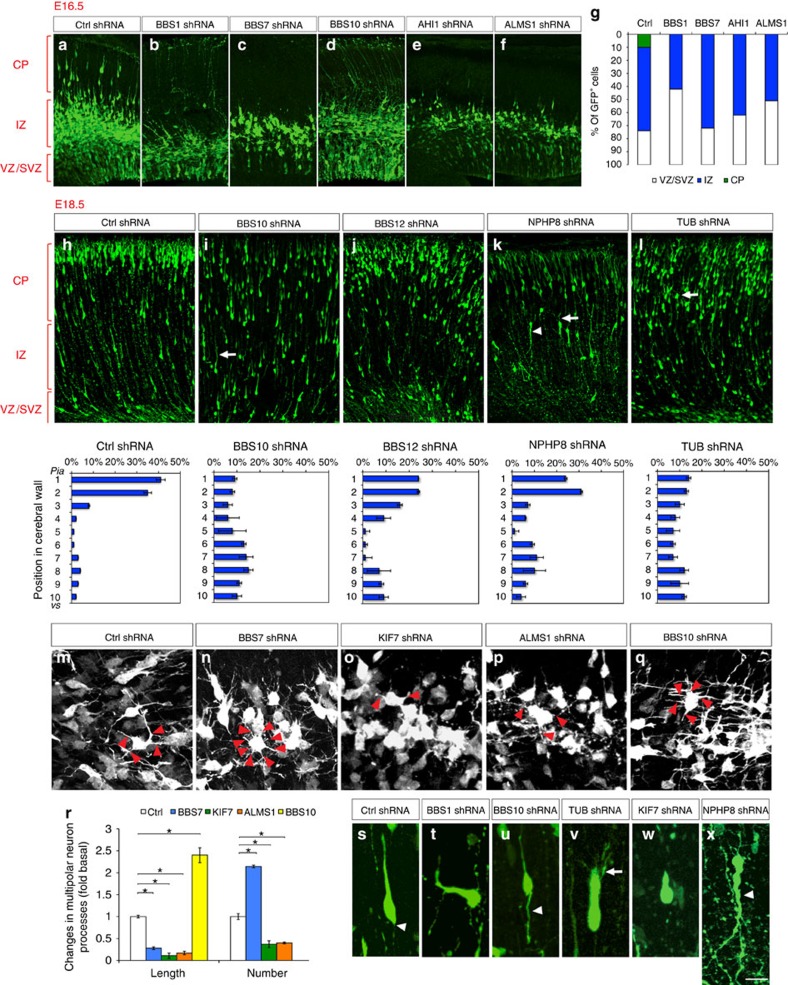
Figure 4. Effect of ciliopathy genes on neuronal migration.
(a–l) GFP+ neurons express shRNAs against BBS1 (b), BBS7 (c), BBS10 (d,ji)i, AHI1 (e), ALMS1 (f), RTTN (i), BBS12 (j) and NPHP8 [RPGRIP1L] (k) and TUB (l) shRNAs do not migrate normally. shRNAs were electroporated at E14.5. a–f and h–l are from cortical analyses at E16.5 and E18.5, respectively. Arrows in i, k and l indicate branched leading processes. Arrowhead in k indicates a misoriented leading process. (g) Quantification of GFP+ cell position in the developing cortical wall (E16.5). Quantification of GFP+ cell position in the developing cerebral wall (E18.5) are shown under each panel in h–l. (m–q) Higher-magnification images of GFP+ multipolar neurons in control, BBS7, KIF7, ALMS1 and BBS10 shRNA groups. Red arrowheads indicate processes. (r) Quantification of average number and length of process in GFP+ multipolar neurons in control and BBS7, KIF7, ALMS1 and BBS10 shRNA groups. Data shown are mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). (s–x) Representative images of GFP+ migrating neurons from control and BBS1, BBS10, TUB, KIF7 and NPHP8 [RPGRIP1L] shRNA groups. Arrowhead, trailing process of migrating neurons. Number of brains per group=4. CP, cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bar, 60 μm (a–f); 65 μm (h–l); 15 μm (m–x).