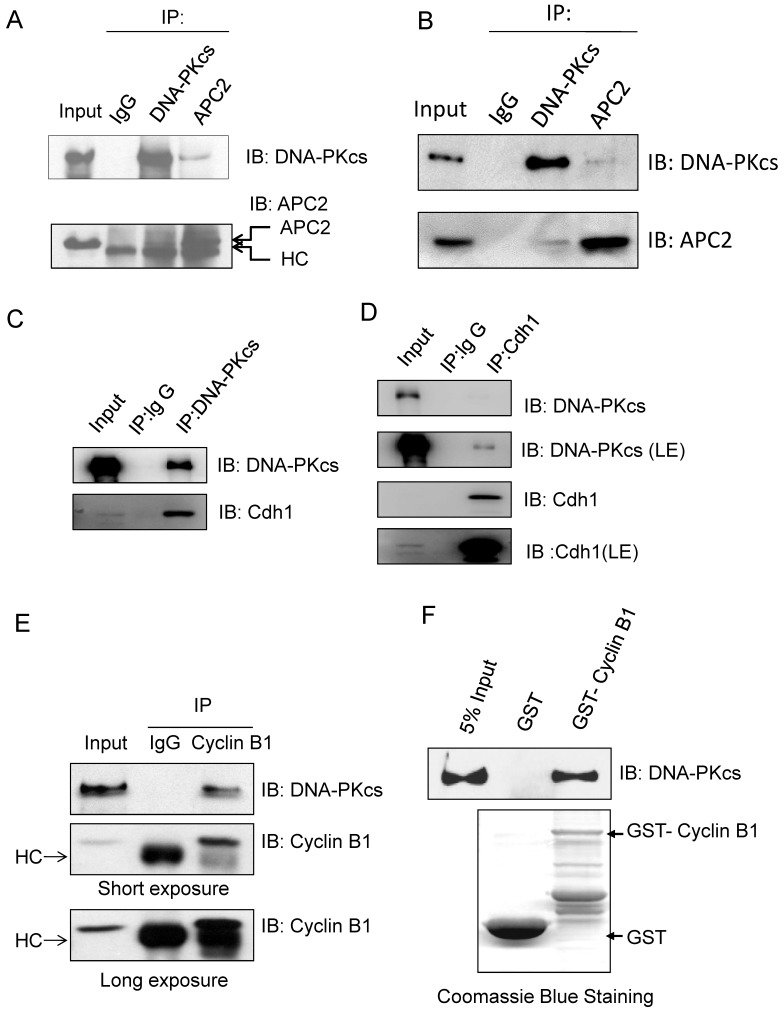
Fig 4.
Immunoprecipiation demonstrates the interaction of DNA-PKcs with APC/C co-activator and Cyclin B1. (A) DNA-PKcs interacts with APC2 in the cells' extract. Co-immunoprecipitation (CoIP) was performed using an antibody against DNA-PKcs or APC2, and the CoIP products were subjected to immunoblotting assay as indicated. (B) Repeat experiment on the interaction of DNA-PKcs with APC2. In order to eliminate the non-specific signal, the EasyBlot anti-rabbit IgG was used in this assay. This anti-IgG is an HRP-conjugated second step reagent that specifically reacts with the native, non-reduced form of mouse IgG and does not bind the reduced, denatured form IgG from the denatured Gel. (C, D) DNA-PKcs interacts with Cdh in the cells' extract. The Co-immunoprecipitation (CoIP) was performed using an antibody against DNA-PKcs (C) or Cdh1 (D), and the CoIP products were subjected to immunoblotting assay as indicated. (E) DNA-PKcs interacts with Cyclin B1 in the cells' extract. The Co-immunoprecipitation (CoIP) was performed using an antibody against Cyclin B1, and the CoIP products were subjected to immunoblotting assay of DNA-PKcs and Cyclin B1. (F) GST pull-down assay demonstrates the direct interaction of DNA-PKcs with GST-PLK1 in vitro and the lack of interaction with GST.